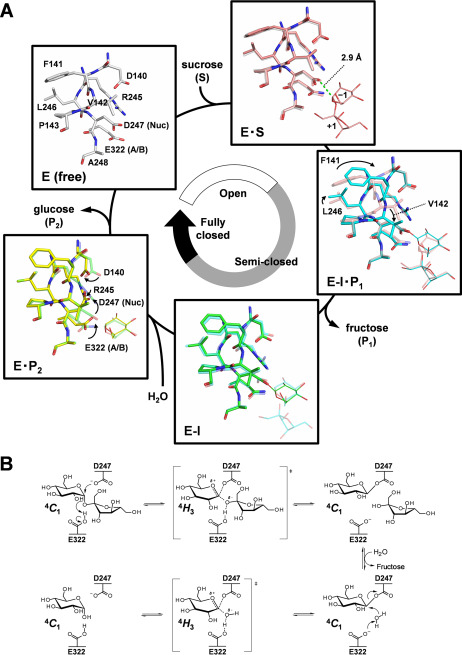
Figure 3.
Complete structural mechanism of sucrose hydrolysis by BmSUH. A, conformational changes in the active site during sucrose hydrolysis. E, enzyme; S, substrate; I, covalent intermediate; P1, product fructose; P2, product glucose; A/B, acid/base catalyst; Nuc, nucleophilic catalyst. The amino acid residues of E (white), E·S (pink), E-I·P1 (cyan), E-I (green), and E·P2 (yellow) states are indicated as sticks and their ligands as thin sticks. The distance between an oxygen atom of Asp247 nucleophilic catalyst and C1 atom of the glucose residue of substrate in the Michaelis (E·S) complex is shown as a green dashed line. The stick models of amino acid residues in a preceding state are superposed for transparency, and arrows indicate conformational changes of the residues. B, conformational itinerary of glucose during BmSUH hydrolytic reaction.