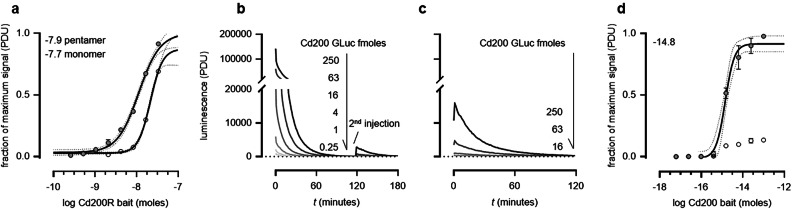
Figure 3.
Reaction-induced inactivation of Gaussia luciferase enables the use of a single construct as both a bait and a prey. (a) Pentameric prey proteins can be used as a bait for sensitive interaction detection. Biotinylated Cd200R Gaussia luciferase-tagged pentamer (filled circles) or monomers (empty circles) were serially diluted and immobilised on a streptavidin-coated microtitre plate as bait proteins and probed for interactions with a beta-lactamase-tagged Cd200 pentamer. (b) Coelenterazine was added to a dilution series of purified Cd200 Gaussia luciferase pentamer which elicited a strong luminescence signal that was gradually lost after around an hour. A second administration of substrate did not generate the same bright luminescence signal. (c) Gaussia enzymatic activity is not restored after a nickel-affinity purification of the inactivated luciferase. Reaction inhibited Gaussia luciferase was purified using Ni–NTA agarose beads with several wash steps before addition of fresh coelenterazine (100 pmol). (d) Pentameric (non-biotinylated) Cd200 Gaussia luciferase prey was probed against biotinylated and inactivated pentameric Cd200R Gaussia luciferase bait (filled circles). The Cd200 prey was also probed against a reaction-inhibited pentameric Gaussia luciferase Cd200 protein used as a non-interacting control bait (empty circles). The inflection point for each interpolated curve is displayed as the log baits (moles) value on each graph. Representative experiments shown with n = 3 for each quantity of prey with SEM for each data point and the 95% CI for the interpolated curves.