FIGURE 1.
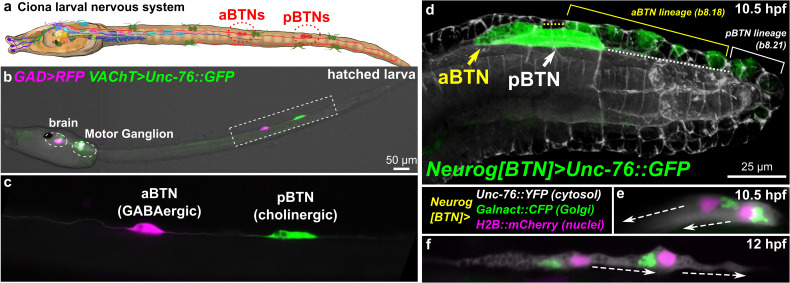
Ciona Bipolar Tail Neurons and the larval nervous system. (a) Cartoon diagram of Ciona larval nervous system based on (Ryan et al., 2016), showing approximate positions of posterior BTNs (pBTN), and anterior BTNs (aBTNs). (b) GAD > RFP (Zega et al., 2008) and VAChT > Unc-76:GFP (Kratsios et al., 2012) reporters label GABAergic aBTNs and cholinergic pBTNs, respectively. Note that due to mosaic incorporation of the reporter plasmids in this particular individual, VAChT > Unc-76:GFP is not expressed in the cholinergic neurons of the core Motor Ganglion, whose axons normally would obscure the BTNs. (c) Magnified view of neurons boxed in (b). (d) Confocal image of migrating BTNs in tail tip of a tailbud (11.5 hpf at 18°C, equivalent to ∼10.5 hpf at 20°C) embryo electroporated with Neurog[BTN] > Unc-76:GFP (green). (e) Relative position of Golgi apparatus is posterior to the nucleus in the BTNs during their migration forward (∼11.5 hpf at 18°C or 10.5 hpf at 20°C), then (f) becomes anterior to each nucleus during distal process extension (∼13.5 hpf at 18°C or 12 hpf at 20°C). Larva diagram illustration by Lindsey Leigh.