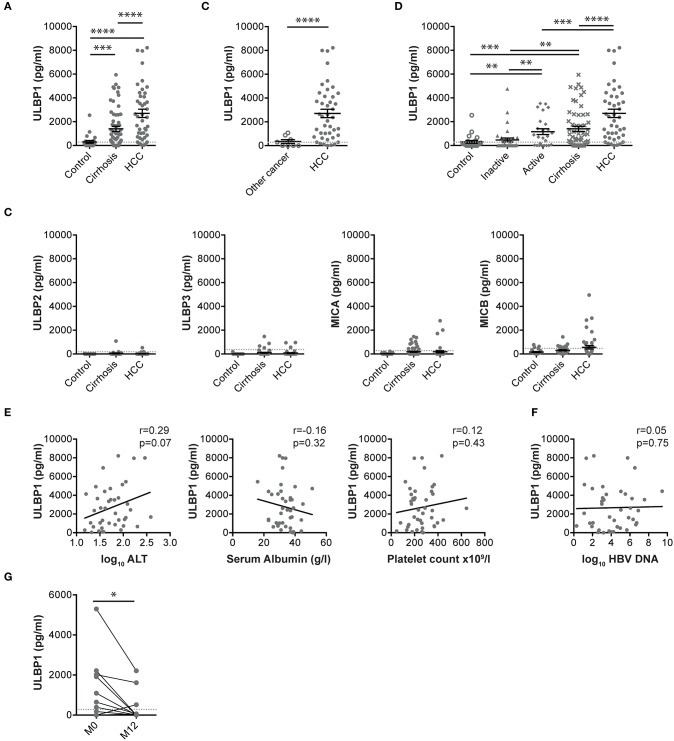
Figure 1.
Serum ULBP1, but not other NKG2D ligands, is raised in patients with HCC in The Gambia. Serum ULBP1 measured by ELISA in patients with HCC (n = 43) in the Gambia compared with controls (n = 23) and patients with cirrhosis (n = 60, A) and other liver tumors (n = 8, B). Other NKG2D ligands in the same cohort (C). Serum ULBP1 in Gambian patients with inactive CHB (n = 34), active CHB (n = 25), or CHB-associated cirrhotic liver disease, HCC and controls (D). Serum ULBP1 concentrations in individuals with HCC against log10 serum ALT concentration (n = 40), serum albumin (n = 42), and platelet count (n = 43) (E) and against log10 HBV DNA concentration (n = 40, F). Paired serum ULBP1 in patients with HBV without HCC before and after 12 months of treatment with tenofovir (n = 50, G). Mean and SEM of all groups shown. Levels of significance: *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.005; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001. Mann Whitney-U test was used for comparisons of two unpaired groups, Spearman rank test was used for correlations of continuous variables, Wilcoxon match-pairs signed rank test was used for comparisons of paired data.