FIGURE 1.
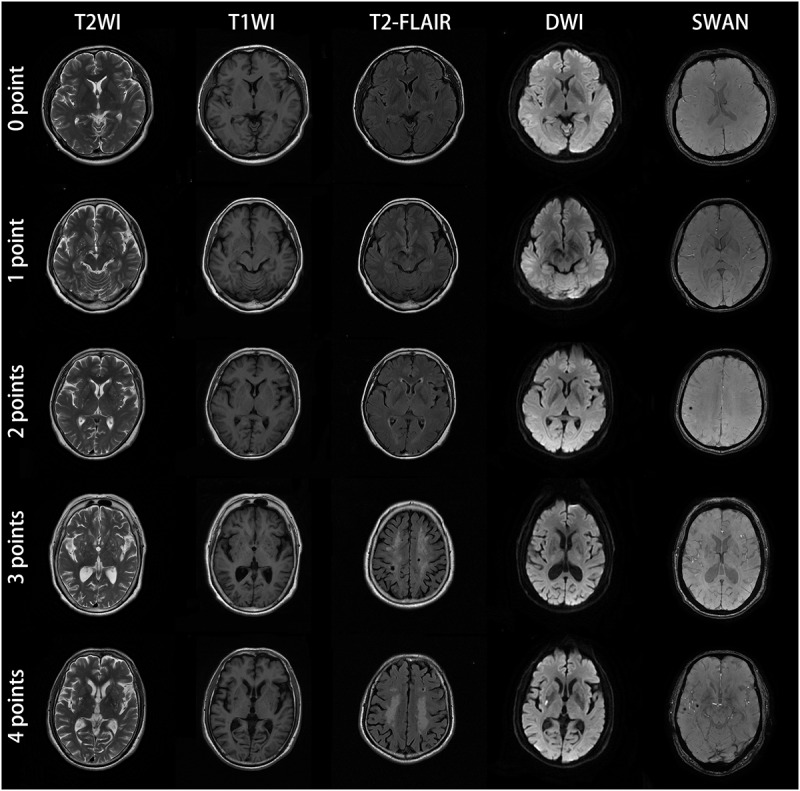
MRI images of subjects with different CSVD total burden score. The subject with score of zero point was a 57-year-old man with no abnormal lesions in MRI images. The patient with score of one point was a 61-year-old female, the bilateral basal ganglia represented punctate and linear lesions with diameter less than 3 mm, hypointensity on T1WI, hyperintensity on T2WI and low signal intensity on T2-FLAIR. The DWI and SWAN sequences showed no abnormality. The bilateral basal ganglia region coincided with EPVS (grade 2–3). For the patient with score of two points, bilateral basal ganglia showed dotted, linear cerebrospinal fluid signal shadow (diameter < 3mm), T2WI showed high signal intensity, T1WI showed low signal intensity, T2-FLAIR showed low signal intensity, which was consistent with the characteristics of EPVS. SWAN sequence of the right parietal lobe showed low signal intensity with diameter ≤ 10 mm, which conformed to the characteristics of CMBs. This CSVD patient was consistent with two points according to the criteria of total CSVD burden score. The patient with score of three points was a 60-year-old female. MRI showed EPVS (grade 2–3) in the bilateral basal ganglia, large confluent areas WMH (Fazekas 3 for DWMH) and lacunar infarction in the center of bilateral semioval center. SWAN sequences showed no abnormality. The patient with CSVD score of four points was a 62-year-old male. There were EPVS (grade 2–3) in the bilateral basal ganglia, large fused WMH (Fazekas 3 for DWMH) in the center of the bilateral semiovale center, acute lacunar infarction with high signal intensity in the right basal ganglia region in DWI image, and CMBs in the right temporal lobe. All the four kinds of imaging markers appeared in this patient.
