Figure 3. Expression and functional properties of GluN1 splice variants.
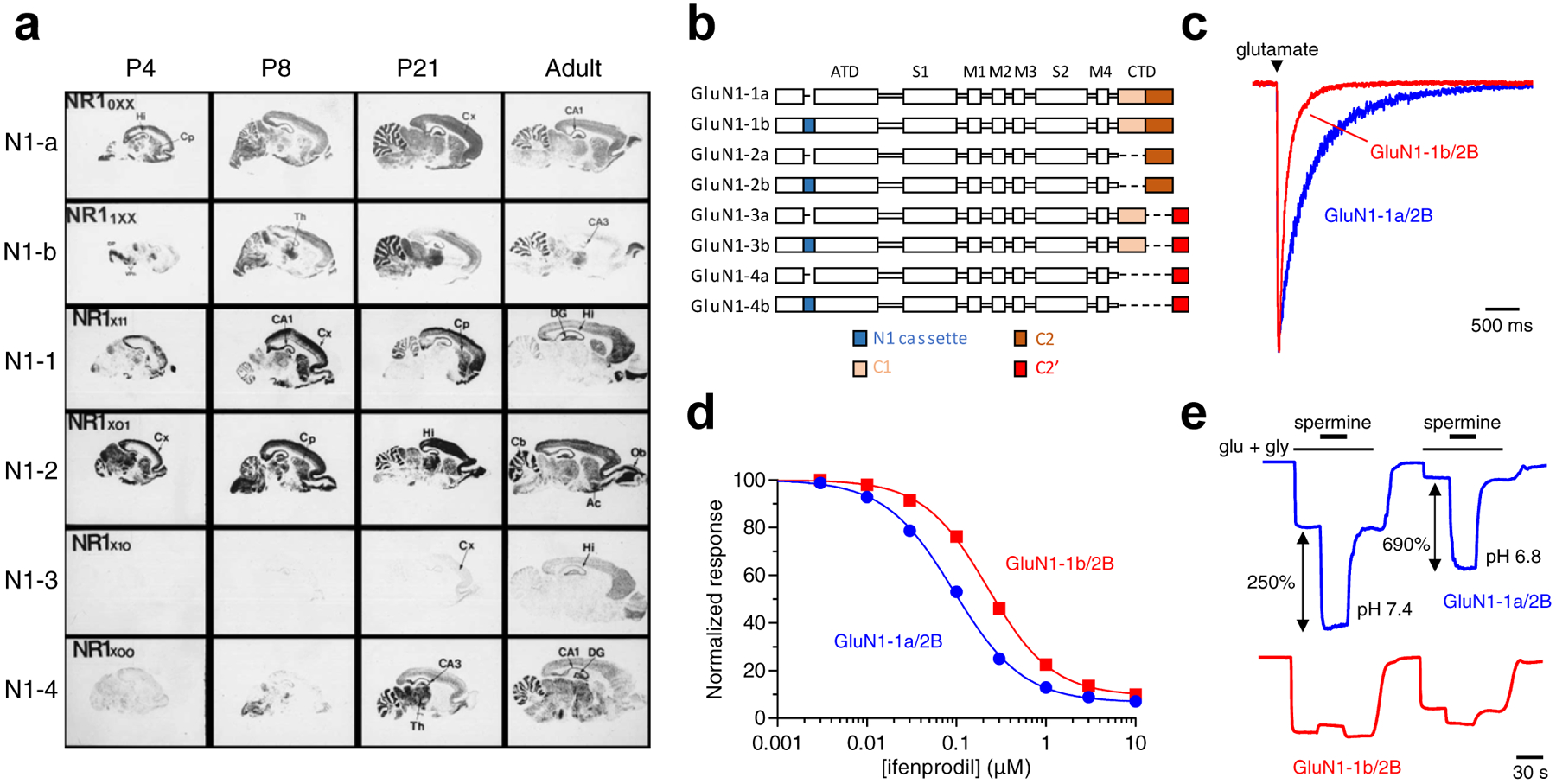
a) Regional and developmental expression of GluN1 splice variants in rat brain revealed in autoradiograms using in situ hybridizations of oligonucleotide probes for the relevant mRNAs to parasagittal sections. Ac, nucleus accumbens; Cb, cerebellum; Cp, caudate-putamen; Cx, cortex; DG, dentate gyrus; DP, dorsal pons; Hi, hippocampus; Ob, olfactory bulb; Th, thalamus; VPn, ventro-posterial thalamic nuclei. Modified with permission from Paupard et al. [78]. b) Linear representation of the GluN1 polypeptide chain for eight alternative splice variants. GluN1 subunits are composed of the amino-terminal domain (ATD), S1 and S2 segments that form the ligand binding domain (LBD), three transmembrane helices (M1, M3, and M4) and a membrane reentrant loop (M2), and the intracellular carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD). The N1 cassette (blue) is 21 amino acids in the ATD encoded by exon 5. The C1 cassette (yellow) is 37 amino acids in the CTD encoded by exon 21, while the C2 cassette (orange) is 38 amino acids in the CTD encoded by exon 22. Deletion of exon 22 creates a shift in the open reading frame, resulting in the alternate exon 22’ that encodes the C2’ cassette (red; 22 amino acids). c) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings of responses from brief application of glutamate (1 ms of 1 mM glutamate) to recombinant GluN1–1a/2B and GluN1–1b/2B receptors expressed in HEK293 cells. NMDA receptors containing exon 5 (e.g. as in GluN1–1b) display faster deactivation time course compared to receptors lacking exon 5 (e.g. as in GluN1–1a). d) Ifenprodil concentration-inhibition relationships for recombinant GluN1–1a/2B and GluN1–1b/2B receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Ifenprodil potency is lower for receptors containing exon 5. e) Representative recordings for spermine potentiation of responses from recombinant GluN1–1a/2B and GluN1–1b/2B receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Spermine sensitivity is dramatically reduced for receptors containing exon 5. Data in c-e) are unpublished from Feng Yi and Kasper B. Hansen.
