Table 3.
Summary of GluN2C/D-selective modulators.
| Activity at GluN1/2X (in μM) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | 2A | 2B | 2C | 2D | |||
| PBPD | 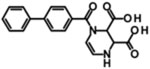 |
Kie | 15.8 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 4.3 | [375] |
| PPDA | 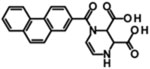 |
Kie | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.096 | 0.125 | [374] |
| UBP141 | 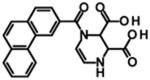 |
Kie | 14.2 | 19.3 | 4.2 | 2.8 | [376] |
| QNZ-46 | 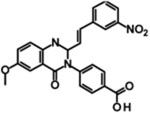 |
IC50 | 229 182 |
ND 193 |
6 7.1 |
3 3.9 |
[383] [384] |
| DQP-1105 | 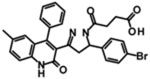 |
IC50 | ND | 113 | 7.0 | 2.7 | [385] |
| CIQ, (+)-CIQ* | 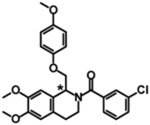 |
EC50 | NE | NE | 2.7, 9.0‡ |
2.8, 8.0‡ |
[390] [391,392] |
| PYD-106 | 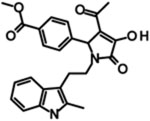 |
EC50 | NE | NE | 16 | NE | [160] |
NE denotes no effect at the highest concentrations evaluated, and ND indicates that the compound displayed some activity, but the affinity or potency could not be determined. Unless otherwise stated (also denoted by †), the values were determined using two-electrode voltage-clamp experiments with Xenopus oocytes.
Ki values were estimated using Cheng-Prusoff correction of the measured IC50 values.
The chiral carbon of (+)-CIQ, the active enantiomer, is denoted by the asterisk in the chemical structure.
The apparent lower potency for (+)-CIQ compared to the racemic mixture is likely due to better estimation of maximum potentiation, since the active enantiomer has increased abundance in solution at concentrations close to the solubility limit (i.e the pure enantiomers can be evaluated at higher concentrations compared racemic CIQ).
