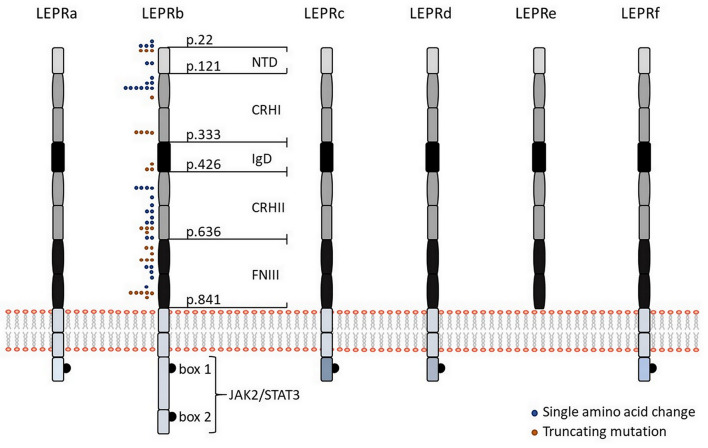
Figure 1.
Leptin receptor isoforms and visualization of mutations in the human LEPR protein. Schematic representation of the six different isoforms of LEPR in humans (LEPRa, b, c, d, e, and f). All isoforms share identical extracellular domains as well as the first 29 amino acids containing box 1 motif for binding of JAK2 of the intracellular domain but they differ in the length and sequence of the C-terminal domain. The intracellular domain of LEPRb contains another JAK binding domain (“box 2”) in addition to a STAT binding site, making LEPRb the predominant isoform responsible for signal transduction. Five of the six isoforms have a transmembrane domain and are generated by alternative mRNA splicing, while the shortest isoform LEPRe is derived by ectodomain shedding at the membrane-spanning domain. Colored dots indicate positions of human LEPR mutations, which result in single amino acid changes (blue dots), or a truncated protein (orange dots), as previously described (38). NTD, N-terminal domain of undefined function; CRHI and CRHII, cytokine receptor homologous domain I and II; IgD, immunoglobulin-like domain; FNIII, fibronectin type 3 domains; JAK2, Janus family tyrosine kinase 2; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.