FIGURE 1.
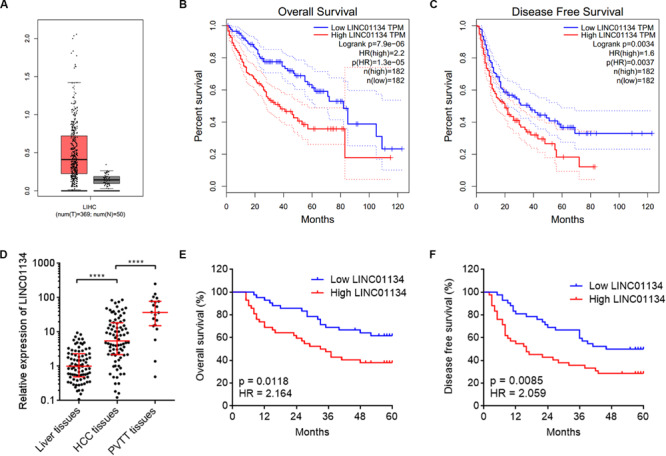
LINC01134 is highly expressed and correlated with poor prognosis of HCC patients. (A) The expression of LINC01134 in HCC tissues (n = 369) versus normal liver tissues (n = 50) from TCGA LIHC dataset. (B) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of the correlation between LINC01134 expression levels and overall survival of HCC patients from TCGA LIHC dataset. (C) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of the correlation between LINC01134 expression levels and disease-free survival of HCC patients from TCGA LIHC dataset. (D) The expression of LINC01134 in 84 pairs of HCC tissues and paired adjacent noncancerous liver tissues and 20 PVTT tissues was detected by qRT-PCR. ****p < 0.0001. The comparison between liver tissues and HCC tissues was calculated by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. The comparison between HCC tissues and PVTT tissues was calculated by Mann–Whitney test. (E) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of the correlation between LINC01134 expression level and overall survival of these 84 HCC patients. p = 0.0118, HR = 2.164 by log-rank test. (F) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of the correlation between LINC01134 expression level and disease-free survival of these 84 HCC patients. p = 0.0085, HR = 2.059 by log-rank test.
