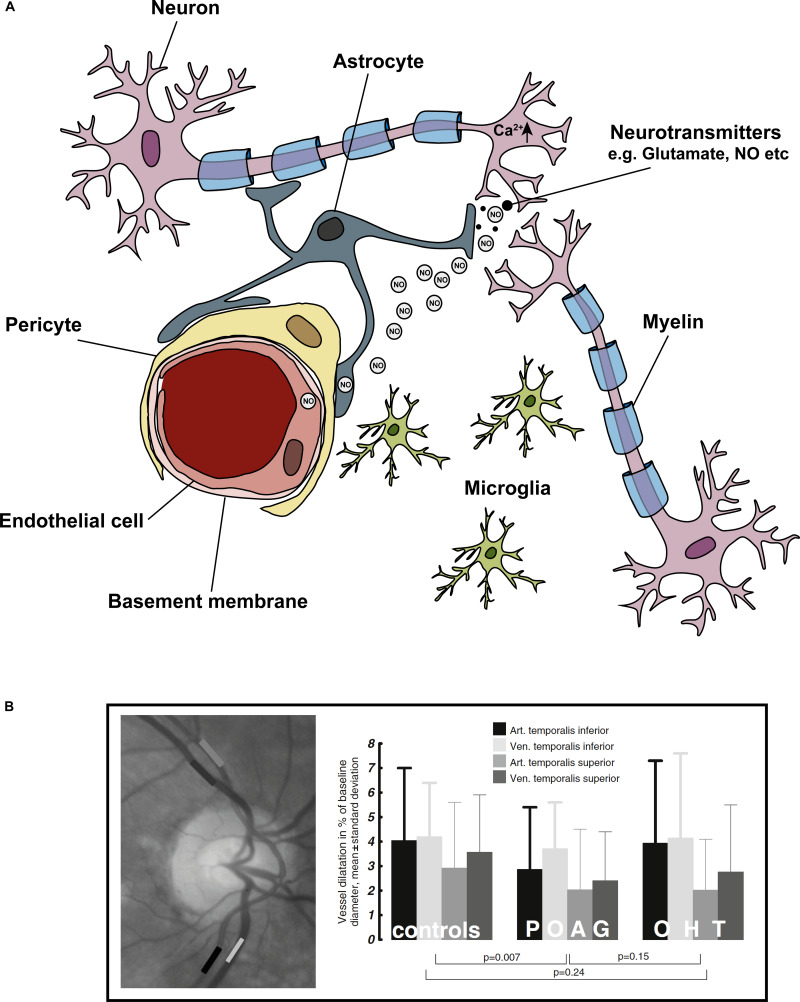
FIGURE 3.
Cells of the ‘neurovascular unit’ and the light flicker response. Neurovascular coupling describes the coupling of neuronal activity to vascular responses. (A) Shows the cells comprising the NVU, these include neurons (in the eye specifically – RGCs), astrocytes, microglia, pericytes, and endothelial cells. In general, a spike in neuronal activity leads to an increase in intracellular Ca2+, which generates NO. NO diffuses to local blood vessel endothelial cells, activating K+ channels, which leads to downstream vasodilation and increased blood flow. The light flicker response demonstrates the tight coupling of neuronal activity (in response to light) and change in vessel diameters in the retina. In glaucoma, this light flicker response is diminished. (B) To measure the light flicker response in the retina, a fundus video is used (image left) where the temporal inferior artery and vein, and temporal superior artery and vein are clearly visible. Areas of analysis are shown in grayscale boxes. Graphical representation the light flicker response in control, ocular hypertension (OHT) and glaucoma patients shows diminished vessel response with disease. Figure adapted from Gugleta et al. (2013b).