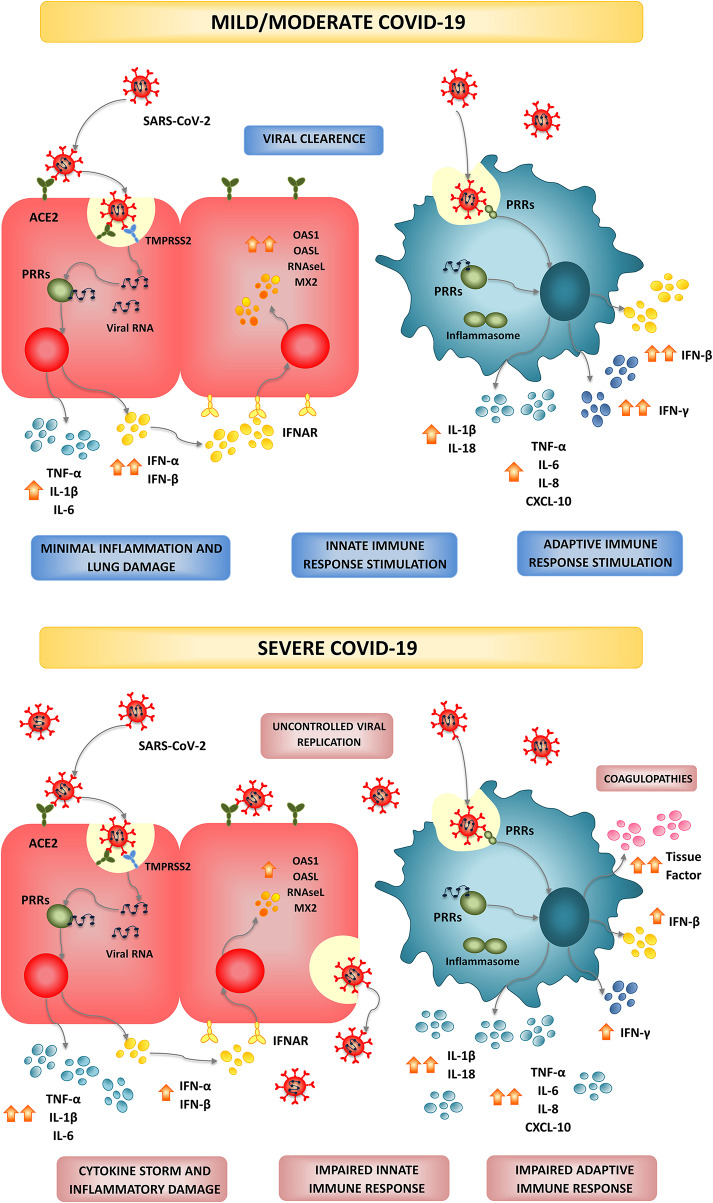
Figure 1.
Infection and modulation of the immune system by SARS-CoV-2. In most individuals, SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers and efficient and timely production of type I IFNs and inflammatory cytokines by epithelial cells and immune cells creating an antiviral state and inducing the recruitment of additional immune cells that collaborate to clear the infection in the lung, with minimal inflammation and damage. This type of immune response is associated to mild or moderate forms of COVID-19 and patients finally recover. In high-risk populations such as the elderly and persons with comorbidities, a dysfunctional immune response is triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection. A severe type of COVID-19 characterized by a cytokine storm that mediates widespread lung inflammation, coagulopathies, organ failure, and death occurs in some patients.