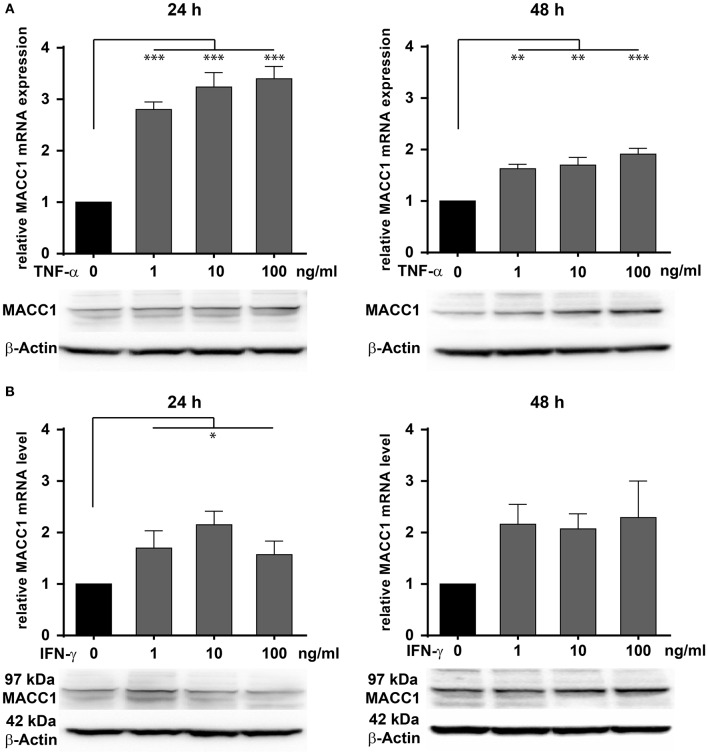
Figure 2.
Effects of TNF-α and IFN-γ stimulation on the MACC1 gene expression. HCT116 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of TNF-α (1, 10, 100 ng/ml) (A) and IFN-γ (1, 10, 100 ng/ml) (B) for 24 h (left side) and 48 h (right side). Cells without cytokine treatment served as controls. MACC1 mRNA expression levels were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Evaluation of MACC1 protein expression levels was performed by Western blot, and β-actin served as loading control. Both pro-inflammatory cytokines can upregulate MACC1 gene expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner. This effect was more pronounced for TNF-α. All experiments were performed as three biologically independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SEM with the statistical significance levels: *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001.