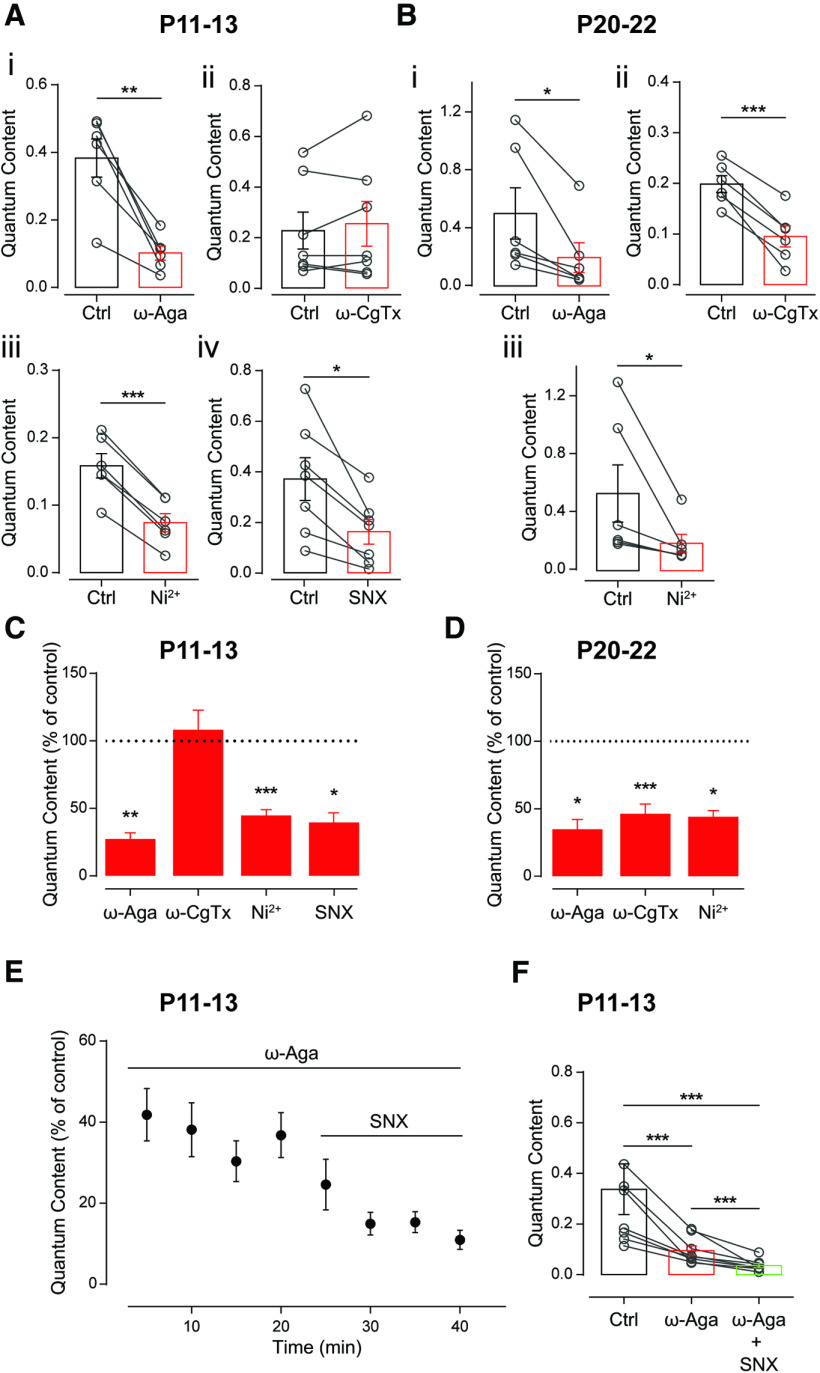
Figure 3.
Differential contribution of VGCCs supporting ACh release at the MOC–OHC synapse at two different postnatal developmental stages. A, B, Effect of 200 nm ω-Aga, 500 nm ω-CgTx, 100 μm Ni2+, and 500 nm SNX, specific blockers of P/Q-, N-, and R-type VGCCs, respectively, on the quantum content of evoked release at P11–P13 (A) and P20–P22 (B). C, D, Summary of the data in A and B, expressed as a percentage of control quantum content. E, F, Time dependence (E) and total effect (F) of the sequential application to the bath solution of 200 nm ω-Aga and 500 nm SNX, specific blockers of P/Q- and R-type VGCCs, respectively, at P11–P13. Values for ω-Aga and SNX shown in F correspond to the last two points of each treatment in E. Paired t test or Wilcoxon rank sum test for A–D; Friedman test followed by Conover post hoc comparisons for F; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.