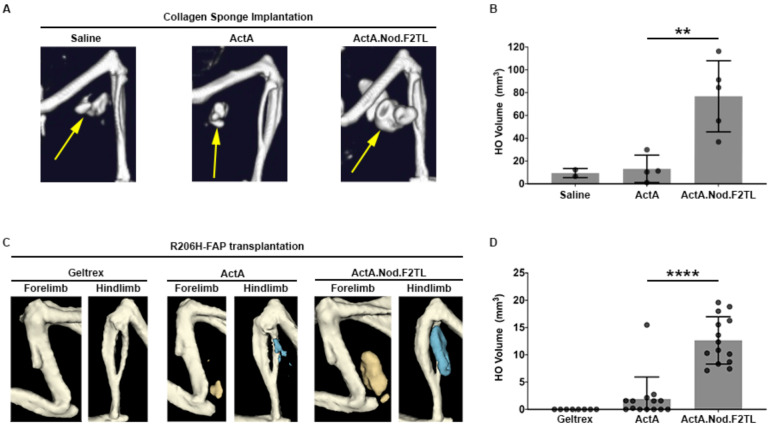
Figure 7. Activin A.Nod.F2TL mutein is a more potent inducer of HO than wild-type Activin A.
(A) Representative µCT images of HO (yellow arrows) from tamoxifen-treated Acvr1[R206H]FlEx/+; Gt(ROSA26)SorCreERT2/+ mice taken 2 weeks after implantation of collagen sponges adsorbed with saline, 20 µg wild-type Activin A (ActA), or 20 µg Activin A.Nod.F2TL (ActA.Nod.F2TL). (B) Quantification of HO volume 2 weeks post-implantation. Saline, n = 2; ActA, n = 4; ActA.Nod.F2TL, n = 5. Each dot represents a single implantation with group mean (grey bar) and ± standard deviation (error bars) shown. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA; **=p ≤ 0.01. (C) Representative µCT images of fore- and hindlimbs from SCID hosts 11 days post-transplantation of FOP FAPs (R206H-FAPs) in Geltrex alone, Geltrex contain 5 µg ActA, or Geltrex containing 5 µg ActA.Nod.F2TL. HO is pseudocolored beige for forelimbs and blue for hindlimbs. (D) Quantification of HO volume 11 days post-transplantation of R206H-FAPs. Geltrex only, n = 8; ActA, n = 14; n = 14; ActA.Nod.F2TL. Each dot represents a single transplantation with group mean (grey bar) and ± standard deviation (error bars) shown. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA; ****=p ≤ 0.0001.
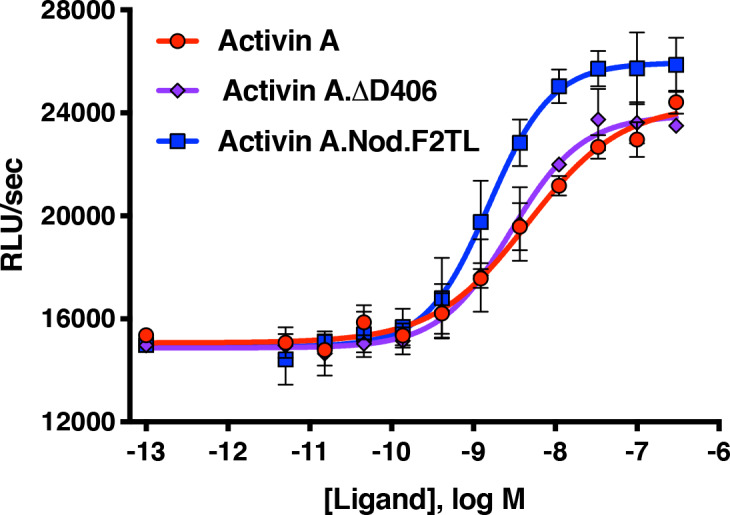
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Activin A F2TL muteins activate ACVR1[R206H] like wild-type Activin A.