Figure 3.
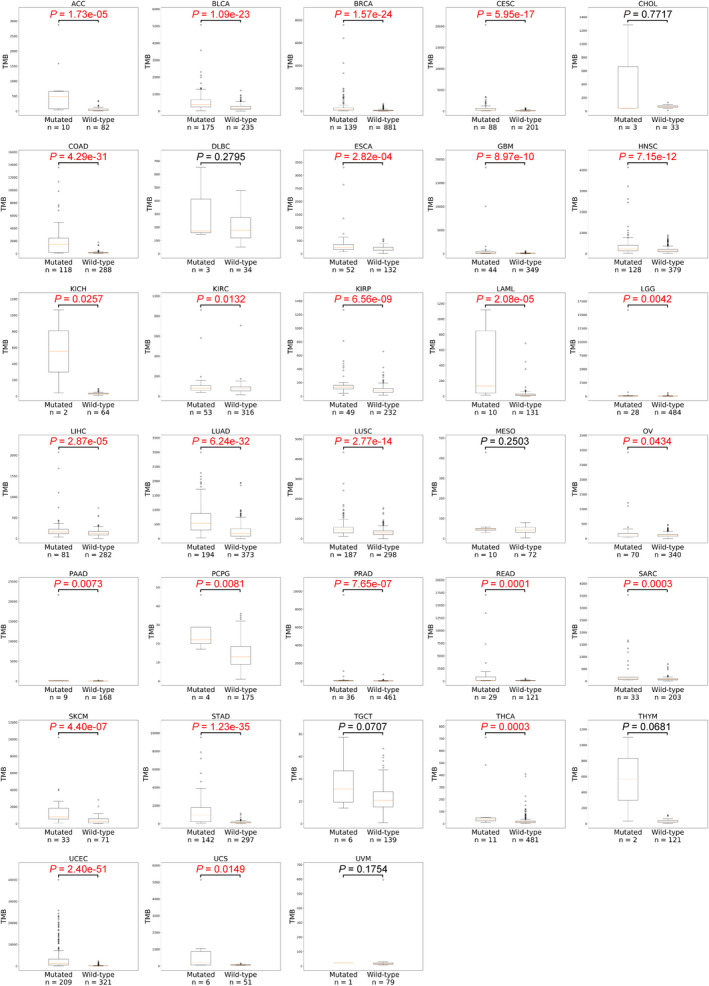
The association of tumor mutation burden and mutations of 18 DDR genes in 33 cancers. TMB (tumor mutational burden) was analysed with (mutated) or without (wild‐type) mutations of 18 DDR genes in 33 cancer from TCGA. Box‐and‐whisker plots depict the distribution of mutation counts. The P‐value was calculated using the Wilcoxon rank‐sum test. The P‐value and sample number in each group are shown. ACC, Adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA, Bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, Breast invasive carcinoma; CESC, Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL, Cholangiocarcinoma; COAD, Colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC, Lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma; ESCA, Esophageal carcinoma; GBM, Glioblastoma multiforme; HNSC, Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH, Kidney chromophobe; KIRC, Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP, Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML, Acute myeloid leukaemia; LGG, Brain Lower Grade Glioma; LIHC, Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, Lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, Lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO, Mesothelioma; OV, Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD, Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG, Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD, Prostate adenocarcinoma; READ, Rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC, Sarcoma; SKCM, Skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD, Stomach adenocarcinoma; TGCT, Testicular germ cell tumors; THCA, Thyroid carcinoma; THYM, Thymoma; UCEC, Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma; UCS, Uterine carcinosarcoma; UVM, Uveal melanoma.
