Fig. 1.
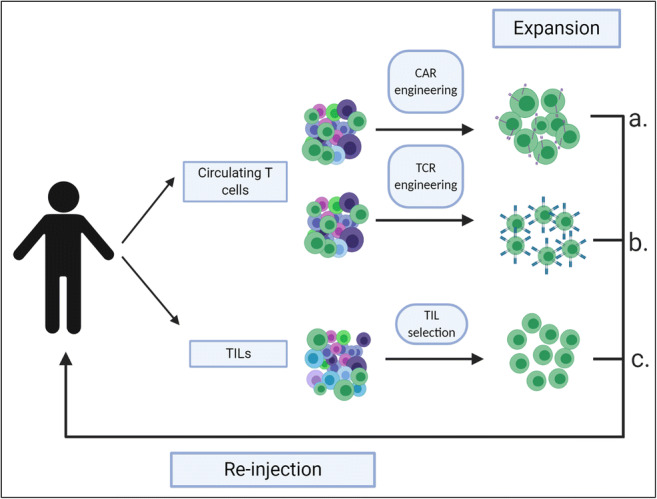
Adoptive T cell transfer therapies. Circulating T cells or tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are collected from a patient’s blood or tumour, respectively. Circulating T cells can be engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) (a.) or T cell receptors (TCRs) (b.) which allow targeting of specific tumour-associated/specific antigens. These modified T cells can be expanded ex vivo and subsequently re-injected into the same patient as an allogeneic therapy. CAR-T cells and TCR-T cells can also be derived from allogeneic sources (not shown), meaning that the donor and the recipient of the cells are different people. Following tumour resection or biopsy, TILs (c.) can be extracted from the tumour material and those with specificity against tumour antigens can be selectively extracted, expanded and re-infused into the patient
