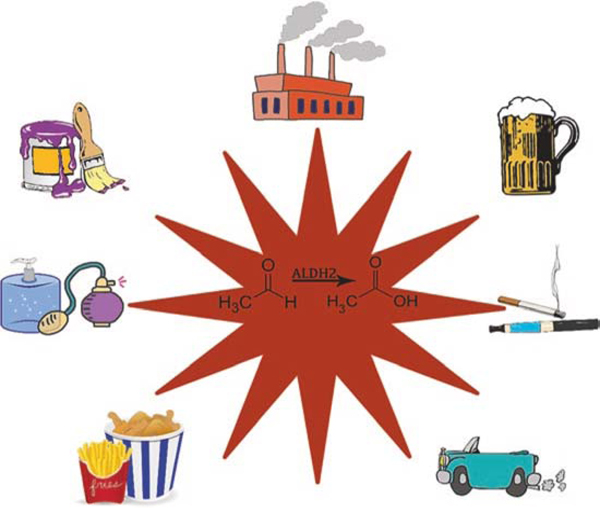
Fig. 1.
Exogenous sources of reactive aldehyde exposure. These include air pollution produced by industrial power plants and automobiles, alcoholic beverages, tobacco products including cigarettes and e-cigarettes, fried foods, cosmetics, and lacquers in paints. As pictured, the ALDH2 enzyme reduces an aldehyde to a less harmful acid. However, for those with an ALDH2*2 variant, the efficiency of this metabolism is reduced by >60%