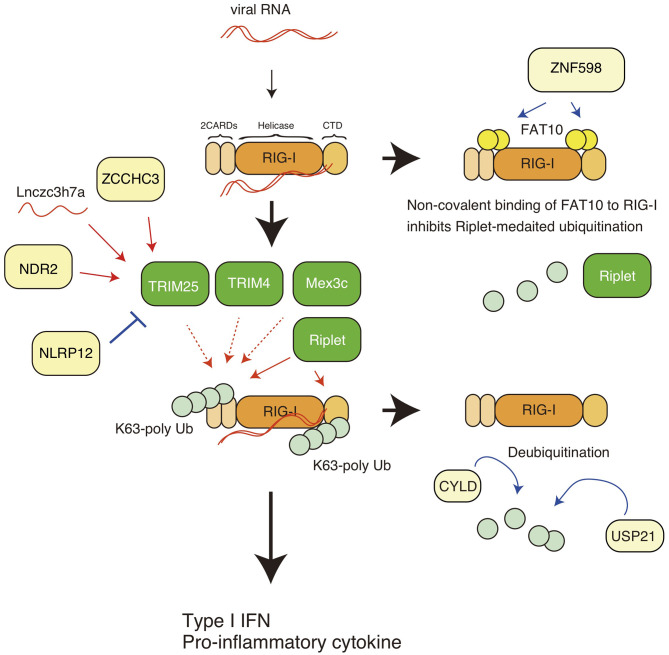
Figure 1.
K63-linked polyubiquitin chain-mediated regulation of RIG-I. The RIG-I protein comprises the N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), an RNA helicase domain, and the C-terminal domain (CTD). K63-linked polyubiquitination leads to activation of RIG-I, leading to the expression of type I IFN and other pro-inflammatory cytokines. TRIM25, Riplet, Mex3c, and TRIM4 are reported to mediate K63-linked polyubiquitination of the CARDs, and Riplet mediates the polyubiquitination of both the CARDs and the CTD. ZNF598 promotes the binding of FAT10 to RIG-I, thereby inhibiting Riplet-mediated ubiquitination of RIG-I. CYLD and USP remove the polyubiquitin chain from RIG-I. The ZCCHC3 and NDR2 protein promote TRIM25-medaited polyubiquitination of RIG-I. A non-coding long RNA, Lnczc3h7a, promotes TRIM25-medated RIG-I activation.