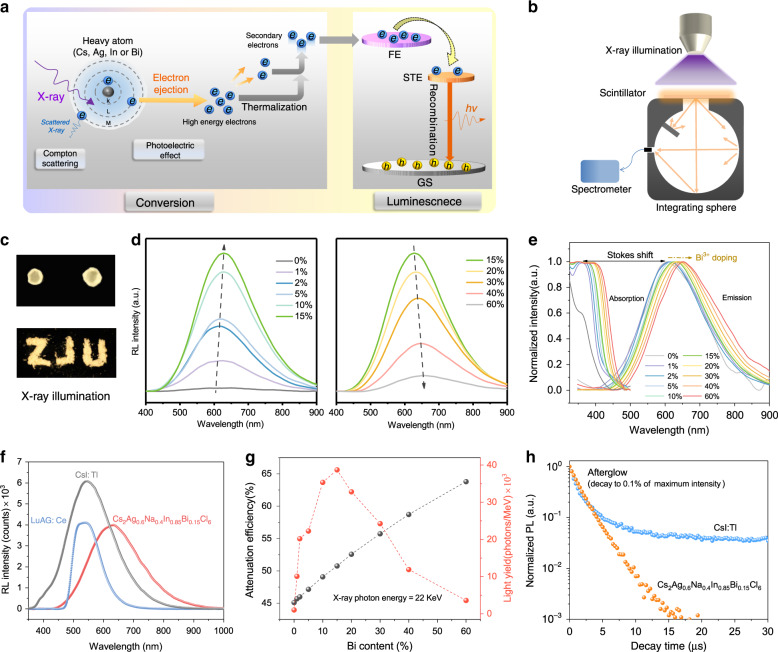
Fig. 2. Radioluminescence (RL) characterisation of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In1-yBiyCl6 scintillators.
a Proposed mechanism of X-ray scintillation in a lead-free halide double-perovskite scintillator. b Schematic of RL spectra measurement using an integrating sphere and a spectrometer with a fixed X-ray source-to-sample distance. c Photographs of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In0.85Bi0.15Cl6 single crystals and powder under X-ray illumination (dose rate: 189 μGyair s−1, voltage: 50 kV). d RL spectra of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In1-yBiyCl6 powder with different Bi3+ contents under X-ray excitation with a dose rate of 189 μGyair s−1 at a voltage of 50 kV. e Stokes shift of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In1-yBiyCl6 with different Bi3+ contents. f RL spectra of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In0.85Bi0.15Cl6, LuAG:Ce and CsI:Tl wafers (dose rate: 189 μGyair s−1, voltage: 50 kV). g Attenuation efficiency and light yield of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In1-yBiyCl6 versus Bi3+ content. h Afterglow curves of Cs2Ag0.6Na0.4In0.85Bi0.15Cl6 and CsI:Tl