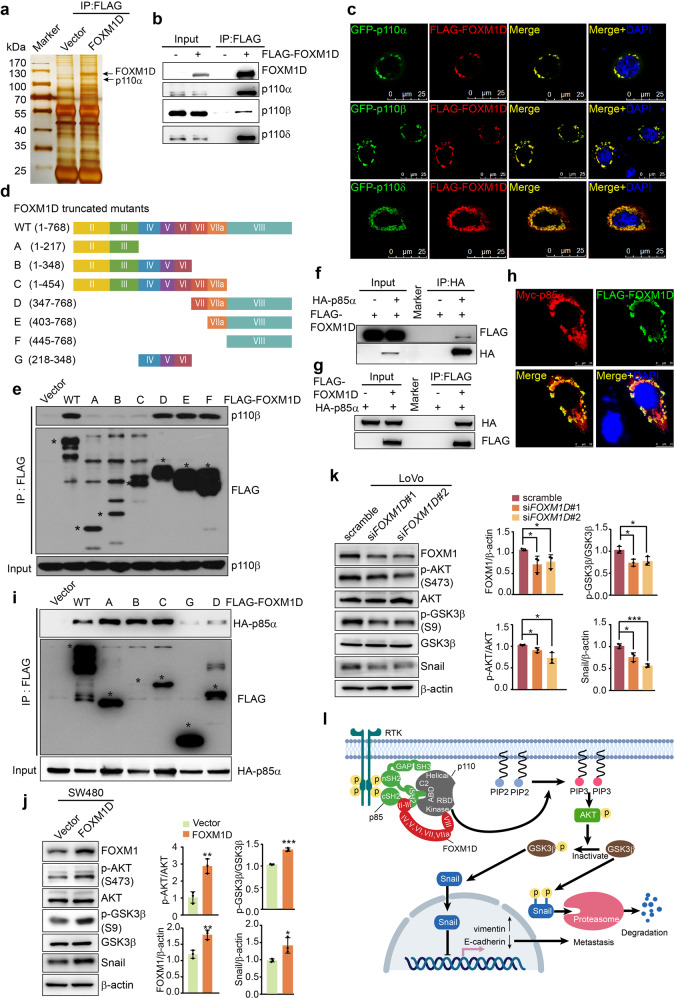
Fig. 1.
FOXM1D directly interacts with p110 and p85 subunits of PI3K and regulates PI3K activity. a The co-IP and silver staining assays to identify the FOXM1D binding proteins in the lysates from HeLa cells expressing FLAG-FOXM1D. b, c The co-IP (b) and ICC (c) assays to determine the interaction between FOXM1D and p110α/β/δ. Scale bar, 25 μm (c). d, e Identification of the mutual binding sites of FOXM1D and p110β. Co-IP assays were performed of the lysates from 293FT cells expressing FLAG-FOXM1D or FLAG-tagged truncated mutants of FOXM1D (d) using a FLAG antibody (e). The obtained samples were detected by IB using FLAG and p110β antibodies (e). f–h The co-IP (f, g) and ICC (h) assays to determine the interaction between FOXM1D and p85α. Scale bar, 10 μm (h). i Identification of the mutual binding sites of FOXM1D and p85α. Co-IP assays were performed of extracts from the 293FT cells expressing FLAG-FOXM1D or FLAG-tagged truncated mutants of FOXM1D (d) and HA-p85α-expressing plasmids using a FLAG antibody (i). The obtained samples were detected by IB using FLAG and HA antibodies (i). j, k The immunoblotting assays to determine the activation of PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/Snail signaling axis in SW480 cells with ectopic FOXM1D expression (j) and in LoVo cells with knocked-down FOXM1D expression (k). Error bars: mean ± SD (n = 3); Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. l The working model. FOXM1D binds to p85 in its junction region between iSH2 and cSH2 via its exon II- and III-encoding region, while binds to p110 kinase domain via its exon VIII-encoding region; therefore, the intermediary FOXM1D generates an effect of steric hindrance between p110 and p85, thus relieving the inhibitory effect of p85 on p110 kinase activity and enhancing the PI3K/AKT activation upon upstream signaling stimulation, which leads to increased phosphorylated GSK3β, stabilized Snail and accumulated nuclear Snail, contributing to the transcriptional repression of E-cadherin and elevation of vimentin, and cancer metastasis. GF growth factor, RTK receptor tyrosine kinase