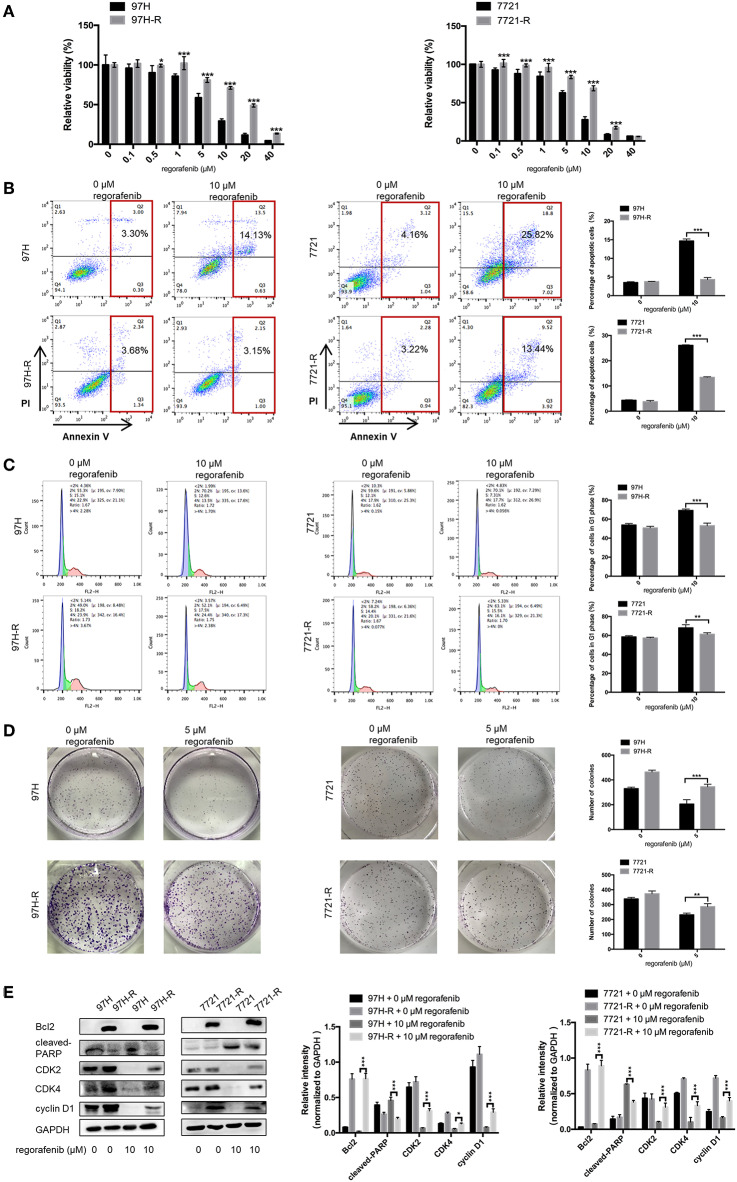
Figure 1.
Establishment of regorafenib-resistant HCC cells. (A) The CCK-8 assay was used to compare the effects of regorafenib on cell proliferation between parental and regorafenib-resistant HCC cells. (B) The percentage of apoptotic parental and regorafenib-resistant HCC cells treated with or without 10 μM regorafenib for 48 h was determined by annexin V/PI staining. (C) The cell cycle distribution of parental and regorafenib-resistant HCC cells treated with or without 10 μM regorafenib for 48 h was detected by flow cytometry. (D) The colony formation activity and the cell proliferation of parental and regorafenib-resistant HCC cells treated with or without 5 μM regorafenib (14 days for SMCC-7721 and 7721-R; 10 days for MHCC-97H and 97H-R, respectively) were measured. (E) The expression levels of Bcl2, cleaved PARP, cyclin D1, CDK2, and CDK4 were examined by Western blot analysis. 7721 and 97H indicate SMMC-7721 and MHCC97H parental cells, respectively; 7721-R and 97H-R indicate regorafenib-resistant SMMC-7721 and regorafenib-resistant MHCC97H cells, respectively. The result is representative for three independent experiments. The error bars represent mean ± SD from a representative experiment. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.