FIG 1.
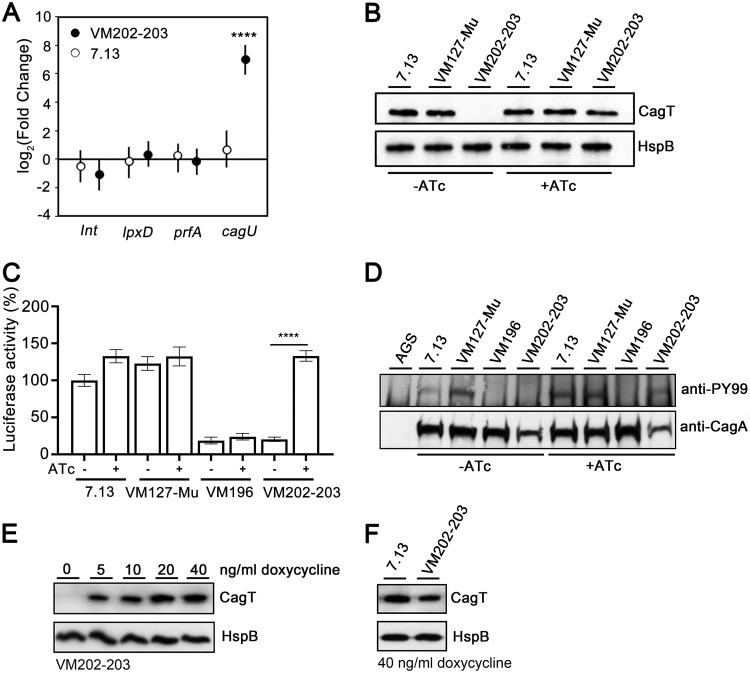
Regulatory control of cagU expression and Cag T4SS activity in vitro. (A) Transcript abundance of cagU and control genes (lnt, lpxD, and prfA) were determined as described in Text S1 in the supplemental material. Fold change values compare transcript levels of the indicated genes in H. pylori strain VM202-203 or 7.13 grown in the presence of anhydrotetracycline (ATc) to corresponding transcript levels in the same strains grown in the absence of ATc. Values represent the means and 95% credible limits (error bars). Among the genes tested, only cagU expression changed significantly in the presence of ATc compared with the absence of ATc. Significance was determined by calculating Bayesian z-scores, and a standard z-test was performed to derive two-tailed P values which were corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method (with a false discovery rate of 5%). ****, P ≤ 0.0001. (B) Western blot detection of CagT protein in the indicated strains in the presence (+) or absence (-) of ATc. Heat shock protein (HspB) was analyzed as a loading control. (C) NF-κB activation induced by the indicated strains in AGS reporter cells. Wild-type strains 7.13 and VM127-Mu (containing tetR but not tetO) (Table 1) were used as positive controls and VM196 (cagU mutant) as a negative control. The data represent results of three independent experiments with multiple technical replicates. Values represent means ± standard errors of the means (SEM). Significance was determined using the Mann-Whitney test. (D) CagA translocation into AGS gastric epithelial cells. 7.13 and VM127-Mu strains were used as positive controls and VM196 as a negative control. (E) Western blot detection of CagT in VM202-203 in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations of doxycycline (0 to 40 ng/ml). (F) Western blot detection of CagT in VM202-203 and wild-type strain 7.13 grown in the presence of 40 ng/ml doxycycline.