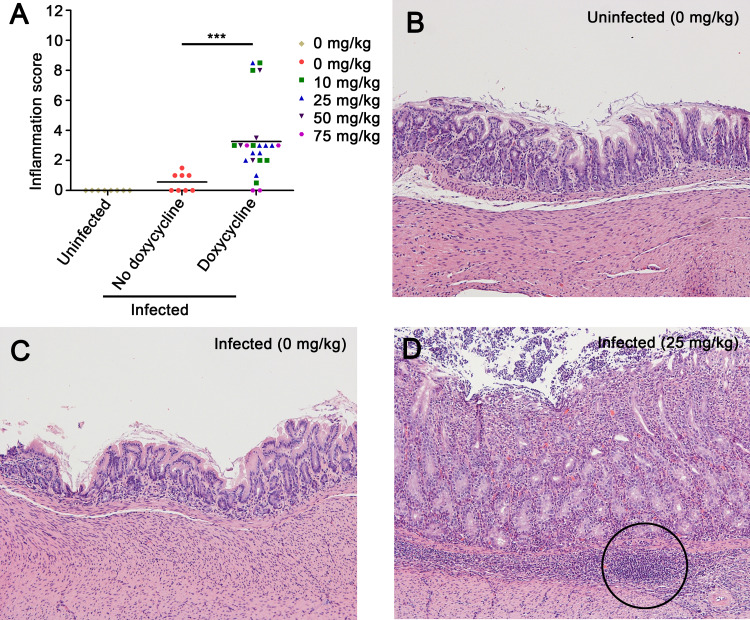
FIG 3.
Gastric inflammation in H. pylori-infected animals in response to Cag T4SS activity. Gerbils were infected with H. pylori VM202-203 and fed diets containing a range of doxycycline concentrations as described in the legend to Fig. 2. (A) Inflammation scores in gastric mucosa. Gastric inflammation was scored on a 12-point scale as described in Materials and Methods. The data represent results for individual animals. Significance was calculated using Mann-Whitney test. ***, P ≤ 0.001. (B to D) Gastric antral histology from representative animals, showing normal histology in uninfected gerbils (B) and infected gerbils receiving a drug-free diet (C). (D) Severe gastric inflammation and lymphoid follicles (circle) were observed in infected gerbils receiving chow containing 25 mg/kg doxycycline. Magnification, 100×.