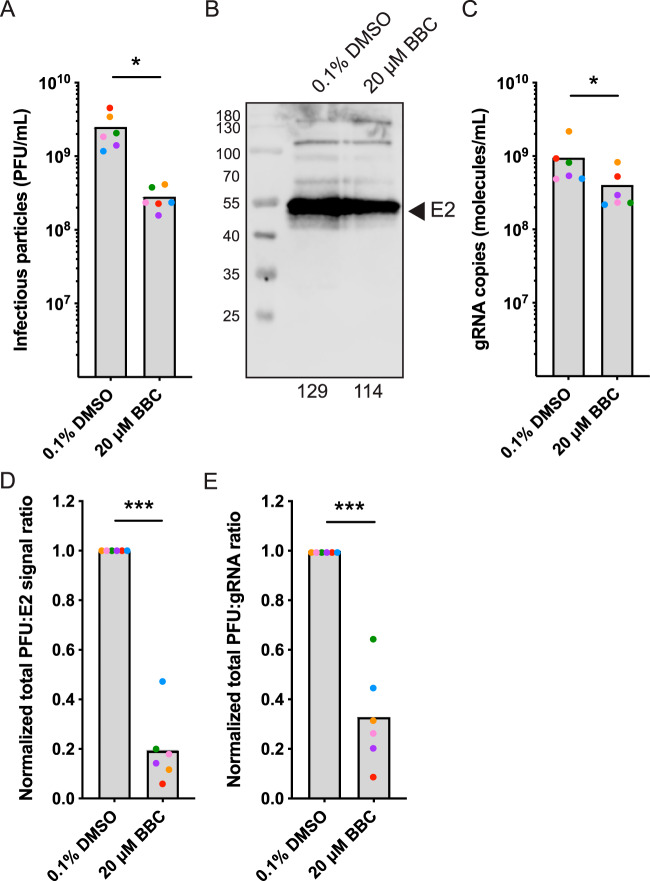
FIG 3.
BBC treatment of infected cells decreases virus specific infectivity. BHK-21 cells were infected with SFV at an MOI of 10 and treated with 0.1% DMSO or 20 μM BBC at 4 hpi, and the cell media were collected at 8.5 hpi. (A) An aliquot of each sample was used to determine infectious particle number by plaque assay. The remaining sample was pelleted through a 20% sucrose cushion and resuspended in buffer. Parallel aliquots were analyzed for particle amounts by (B) SDS-PAGE and WB using a MAb to E2 or (C) used for RNA isolation and gRNA quantitation by RT-qPCR. For specific infectivity determination, the ratio of total infectious particle number to absolute E2 signal or to absolute gRNA copies (D and E, respectively) was expressed relative to DMSO treatment. The graphs represent the means with individual data points plotted for six independent experiments. Individual data points are paired for each treatment for each replicate, and paired points are displayed in the same color. The representative E2 WB and the quantitated signal displayed below in panel B is the sample corresponding to the orange point in panels A, C, D, and E. To assess the statistical significance between DMSO versus BBC treatment, two-tailed Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank tests were performed in panels A and C and two-tailed paired t tests were performed in panels D and E. ***, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05.