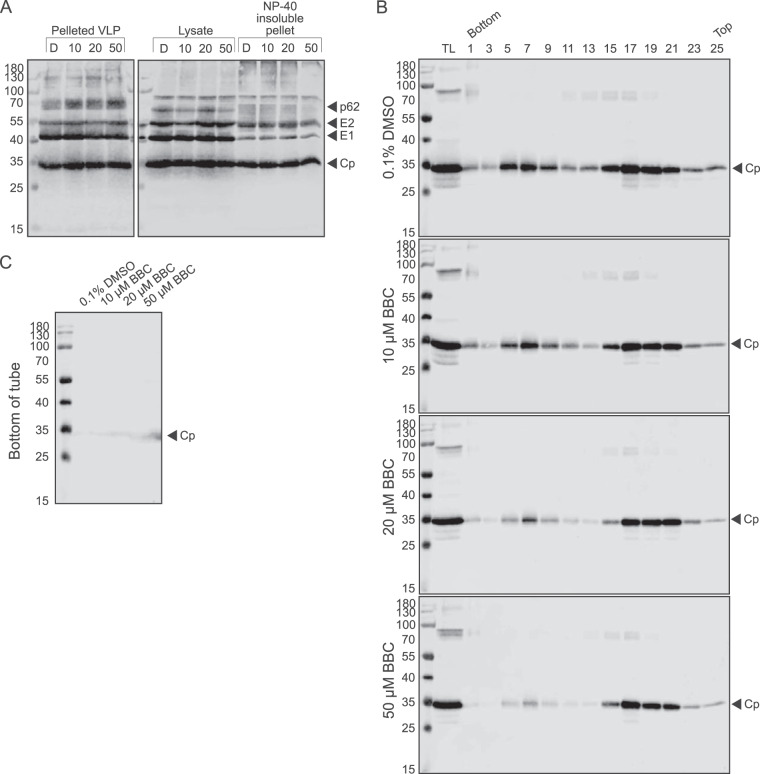
FIG 5.
BBC treatment of VLP-producing cells decreases stable cytoplasmic nucleocapsids. (A) VLP and steady-state structural protein production. BHK-21 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding the SFV structural proteins. At 22 h posttransfection, cells were washed and incubated with DMSO or BBC for 8 h. VLPs in the medium were pelleted through a 20% sucrose cushion, and cells were solubilized in NP-40-containing lysis buffer and centrifuged to obtain detergent-insoluble pellets and lysates. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and WB using PAb to E2 and E1 and MAb to Cp. Treatment labels are as follows: D, 0.1% DMSO; 10, 10 μM BBC; 20, 20 μM BBC; 50, 50 μM BBC. The results shown are representative of four independent experiments. (B and C) Gradient analysis of VLP cytoplasmic nucleocapsids. BHK-21 cells were treated as in panel A, and cell lysates were separated by iodixanol density gradient sedimentation. (B) Alternating fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and WB analysis using PAb to Cp. TL represents equivalent aliquots of the total cell lysates; cytoplasmic nucleocapsids are in fractions 5 to 9, and fractions 17 to 21 represent Cp bound to ribosomes. (C) The bottom of the tube was washed with SDS sample buffer to collect any Cp-bound complexes that pelleted through the 50% iodixanol cushion and analyzed as in panel B. The results shown in panels B and C are representative of three independent experiments.