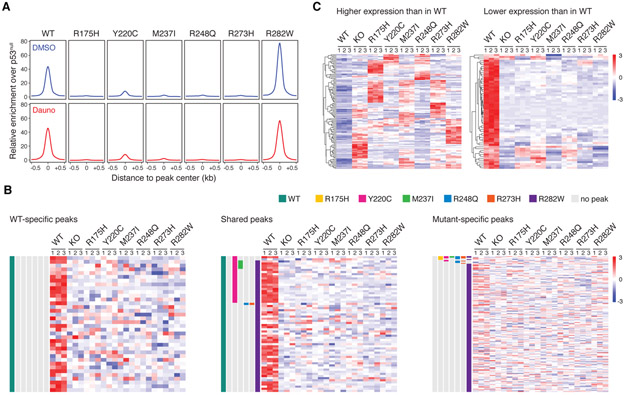
Fig. 2. Transcriptional consequences of TP53 hotspot missense mutations in isogenic AML cell lines.
(A) Genome-wide relative enrichment of wildtype and missense mutant p53 variants (ChIP for wild-type or missense mutant p53 over ChIP in p53−/− cells) over transcriptional start site (TSS)-proximal regions (−10kb – first intron) in K562-TP53 isogenic cell lines upon treatment with DMSO or 100nM daunorubicin for 24 or 6 hours, respectively. (B) Heatmap depicting normalized expression of genes associated with WT-specific (left), shared (middle), and p53 mutant-specific (right) ChIP-seq peaks in K562-TP53 isogenic cell lines treated with 100nM daunorubicin for 24 hours (experimental replicates n=3). (C) Heatmap of the pooled top 30 (left) and pooled bottom 30 (right) genes relative to wild-type p53 in K562-TP53 isogenic cell lines treated with 100nM daunorubicin for 24 hours (RNA-seq experimental replicates n=3).