Figure 3. Palmitoylation is critical for ISP1/ISP3 polarization and ookinete differentiation.
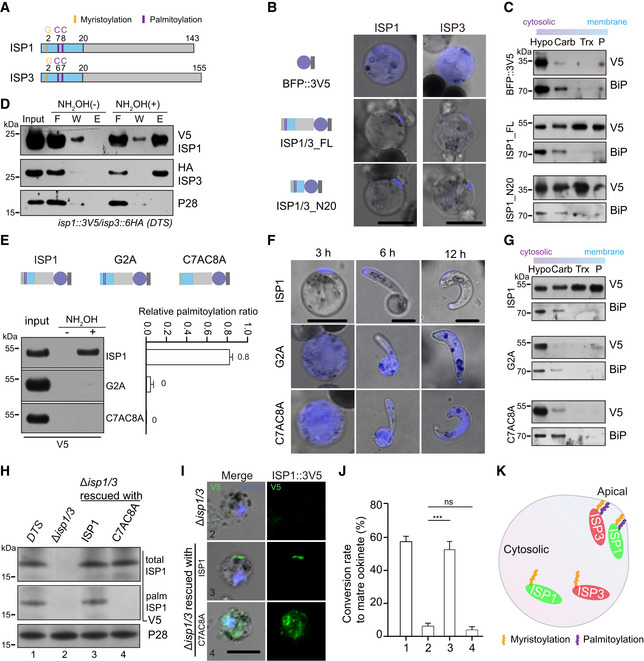
- Structure and N‐terminal residues for potential acylation of ISP1 and ISP3.
- Fluorescent microscopy of ISP and its N‐terminal 20 residues (N20) fused with a BFP::3V5 peptide episomally expressed in zygotes. Scale bar = 5 μm.
- Solubility assay detecting membrane association of ISP1_FL and ISP1_N20 using different detergents. Cytosolic soluble proteins are in hypotonic buffer (Hypo), peripheral membrane proteins in carbonate buffer (Carb), integral membrane proteins in Triton X‐100 buffer (Trx), and insoluble proteins in pellet (P). BFP::3V5 is in the soluble fraction, while ISP1_FL and ISP1_N20 are in the membrane‐associated fractions. ER protein BiP is a loading control.
- Acyl‐RAC method detecting palmitoylation of ISP1 and ISP3 in zygotes of the DTS strain. Proteins from F (flow‐through), W (wash), and E (elution) are analyzed. P28 as a loading control.
- Substitutions of N‐terminal cysteine or glycine residues to alanine (G2A or C7A/C8A) ablate palmitoylation of ISP1. ISP1 was fused with BFP::3V5 and episomally expressed in zygotes. Right panel shows quantification of palmitoylated protein band from two independent repeats, and values are means ± SD.
- G2A and C7AC8A mutations cause cytoplasmic distribution of ISP1 during zygote‐to‐ookinete differentiation. Scale bar = 5 μm.
- Membrane association of ISP1 with either G2A or C7AC8A substitutions.
- Expression and palmitoylation of ISP1 in ∆isp1/3 parasites complemented with the 3V5‐tagged WT ISP1 or C7AC8A mutant.
- IFA of ISP1 at zygote of the complemented parasites. Scale bar = 5 μm.
- In vitro differentiation to mature ookinete of the complemented parasites. Values are means ± SEM (n = 4 replicates), two‐tailed t‐test, ***P < 0.001, ns: not significant.
- A model illustrating palmitoylation critical for apical localization of ISP1 and ISP3 at zygote.
Source data are available online for this figure.
