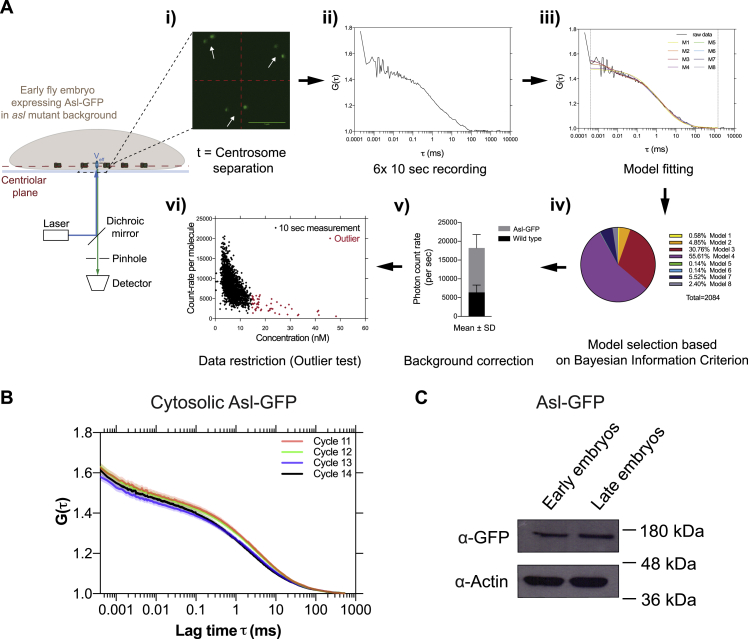
Figure S5.
FCS Analysis of Cytosolic Asl Levels, Related to Figure 3
(A) Schematic workflow describes the acquisition and analysis of point Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS) measurements (see STAR Methods for further details). The 488nm laser beam is positioned at the centriolar plane in embryos expressing 2 copies of Asl-GFP (under the control of its own promoter in an asl mutant background). (i) At the beginning of every cycle, when the old and new mother centrioles have just separated (white arrows), 6x 10 s FCS measurements were taken at a point in the cytosol maximally distant from the centrioles (center of red crosshairs). (ii) This generated 6 autocorrelation functions (ACFs) (a typical example is shown here). (iii) In the FoCuS-point software, 8 different models were fitted to each ACF. (iv) The model that best fitted the majority of the data (#4 in this case) was chosen based on the Bayesian information criterion, and all ACFs were then fitted to this model. (v) The fitted ACFs were corrected for background noise which was determined by measurements in WT embryos. (vi) The ACFs used for further analysis were then restricted by excluding individual outlier measurements based on a ROUT-outlier test (Q = 1%) (these outlier measurements usually had a poor signal-to-noise ratio and gave concentrations that were often biologically unrealistic, and were presumably generated when a centriole or non-specific fluorescent structure passed through the analyzed volume).
(B) Graph shows the average ACFs (represented as Mean ± SEM) for nuclear cycles 11-14 before background corrections. All individual ACFs were used to calculate the cytosolic concentration data shown in Figure 3D.
(C) Western blot shows the protein levels of the Asl-GFP in either the early or late cell cycles from embryos of the same genotype used in (A) and (B). This supports the results obtained from the FCS measurements, and suggests that total Asl levels do not change significantly during the development of the syncytial embryo. Early and late embryos were separated based on their distinct morphology (judged by eye using a dissection microscope). Actin is shown as a loading control. A representative blot is shown from two technical repeats.