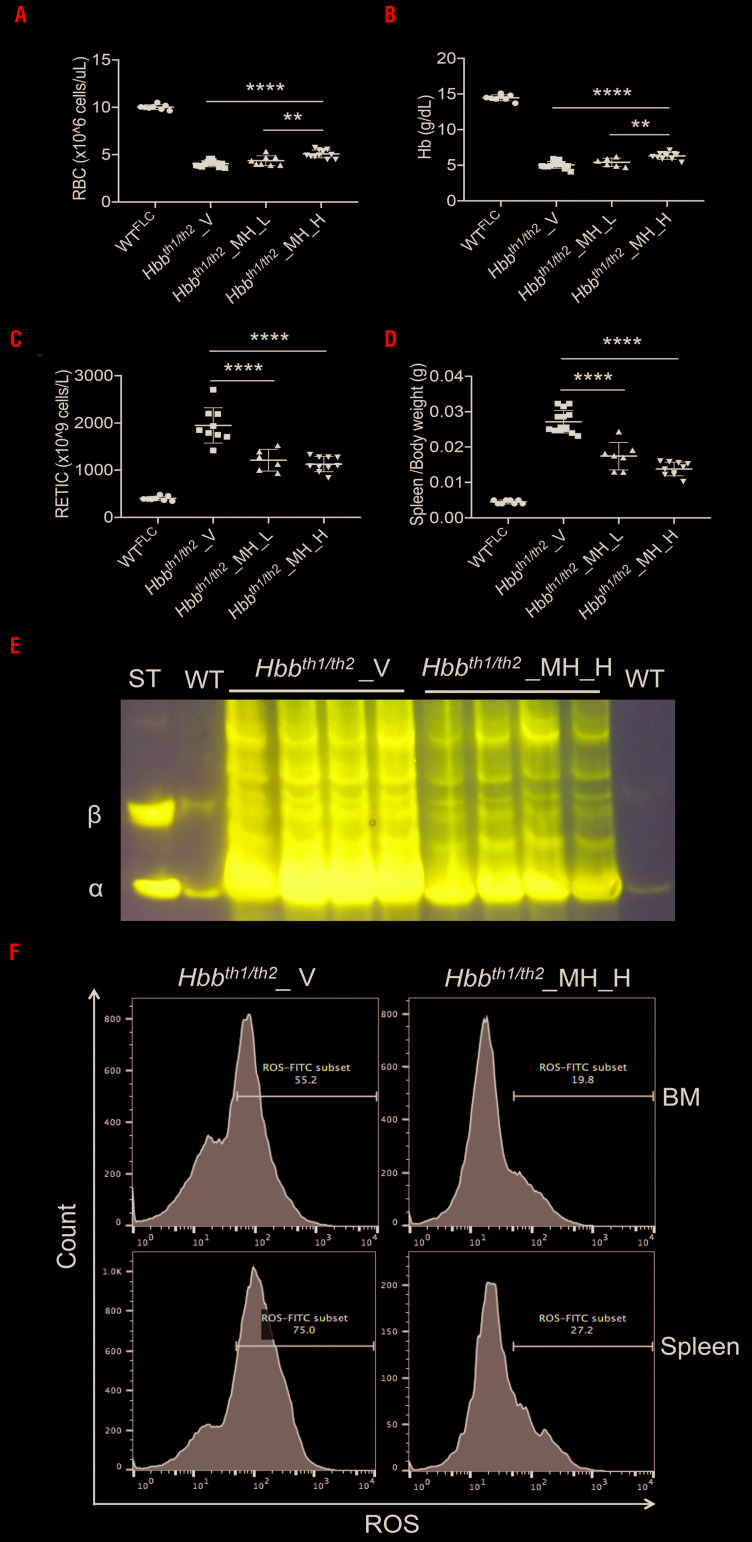
Figure 3.
The effect of minihepcidin on complete blood count and splenomegaly in Hbbth1/th2-BMC mice. Administration of a low dose of minihepcidin (MH_L) (2.625 mg/kg) or a high-dose (MH_H) (5.25 mg/kg) to Hbbth1/th2-BMC mice resulted in dose-dependent increases in (A) red blood cell (RBC) count and (B) hemoglobin (Hb) concentration and decreases in (C) reticulocyte (RETIC) count and (D) spleen weight. Bars represent the standard deviation. ****P≤0.001, **P≤0.01. (E) Minihepcidin administration also decreased hemichrome formation. (F) Flow cytometry studies of bone marrow and spleen erythroid populations of Hbbth1/th2-BMC mice treated with MH_H showed reduced levels of reactive oxygen species. BM: bone marrow; ROS: reactive oxygen species.