Figure 1.
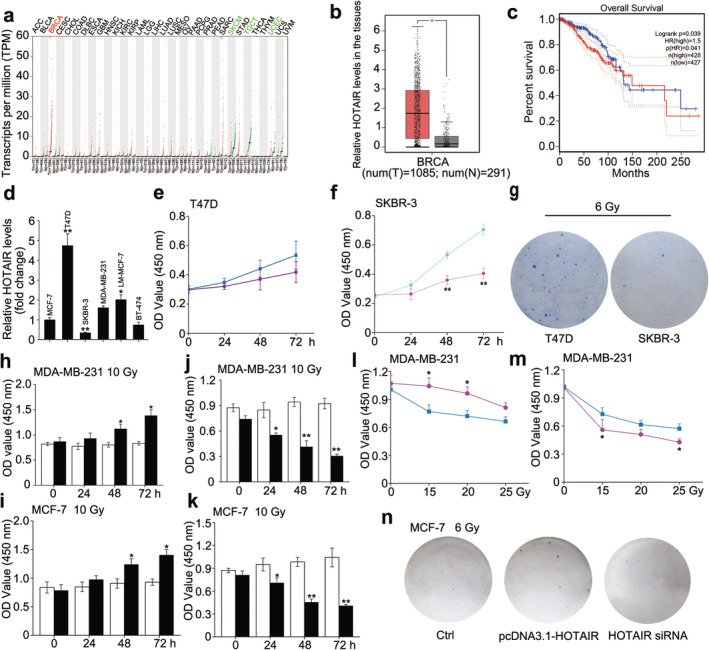
HOTAIR endows breast cancer with radiation resistance. (a–c) The expression profile of HOTAIR in different cancer types and the corresponding normal tissues (a), the relative HOTAIR levels in breast cancer tissues and normal breast tissues ( ) Tumour, (
) Tumour, ( ) Normal (b) and the relationship between HOTAIR levels and overall survival of BRCA patients (
) Normal (b) and the relationship between HOTAIR levels and overall survival of BRCA patients ( ) Tumour, (
) Tumour, ( ) Normal (c) were obtained from the GEPIA database. (
) Normal (c) were obtained from the GEPIA database. ( ) Low HOTAIR TPM, (
) Low HOTAIR TPM, ( ) High HOTAIR TPM (d) The relative abundance of HOTAIR in different BRCA cells was determined by real‐time PCR. (e and f) CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability of T47D (e) (
) High HOTAIR TPM (d) The relative abundance of HOTAIR in different BRCA cells was determined by real‐time PCR. (e and f) CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability of T47D (e) ( ) 0 Gy, (
) 0 Gy, ( ) 10 Gy and SKBR‐3 (f) after 0 or 10 Gy irradiation treatment. (
) 10 Gy and SKBR‐3 (f) after 0 or 10 Gy irradiation treatment. ( ) 0 Gy, (
) 0 Gy, ( ) 10 Gy (g) Colony formation assay was used to measure the proliferative ability of T47D and SKBR‐3 after 6 Gy irradiation treatment. (h and i) MDA‐MB‐231 and MCF‐7 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability after 10 Gy irradiation treatment. (
) 10 Gy (g) Colony formation assay was used to measure the proliferative ability of T47D and SKBR‐3 after 6 Gy irradiation treatment. (h and i) MDA‐MB‐231 and MCF‐7 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability after 10 Gy irradiation treatment. ( ) pcDNA3.1, (
) pcDNA3.1, ( ) pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR (j and k) MDA‐MB‐231 and MCF‐7 cells were transfected with siRNA Ctrl/si‐HOTAIR 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability after 10 Gy irradiation treatment. ; (
) pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR (j and k) MDA‐MB‐231 and MCF‐7 cells were transfected with siRNA Ctrl/si‐HOTAIR 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability after 10 Gy irradiation treatment. ; ( ) siRNA Ctrl, (
) siRNA Ctrl, ( ) HOTAIR siRNA; (l and m) MDA‐MB‐231 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR (l) or siRNA Ctrl/si‐HOTAIR (
) HOTAIR siRNA; (l and m) MDA‐MB‐231 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR (l) or siRNA Ctrl/si‐HOTAIR ( ), pcDNA3.1, (
), pcDNA3.1, ( ) pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR (m) 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability after 0, 15, 20 and 25 Gy irradiation treatment. (
) pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR (m) 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, CCK‐8 assay was used to measure the cell viability after 0, 15, 20 and 25 Gy irradiation treatment. ( ) siRNA Ctrl, (
) siRNA Ctrl, (
 ) HOTAIR siRNA (n) MCF‐7 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 + siRNA Ctrl/pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR/si‐HOTAIR 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, then colony formation assay was used to measure the proliferative ability after 6 Gy irradiation treatment. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significant differences are indicated: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t‐test.
) HOTAIR siRNA (n) MCF‐7 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 + siRNA Ctrl/pcDNA3.1‐HOTAIR/si‐HOTAIR 12 hours before the irradiation treatment, then colony formation assay was used to measure the proliferative ability after 6 Gy irradiation treatment. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significant differences are indicated: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t‐test.
