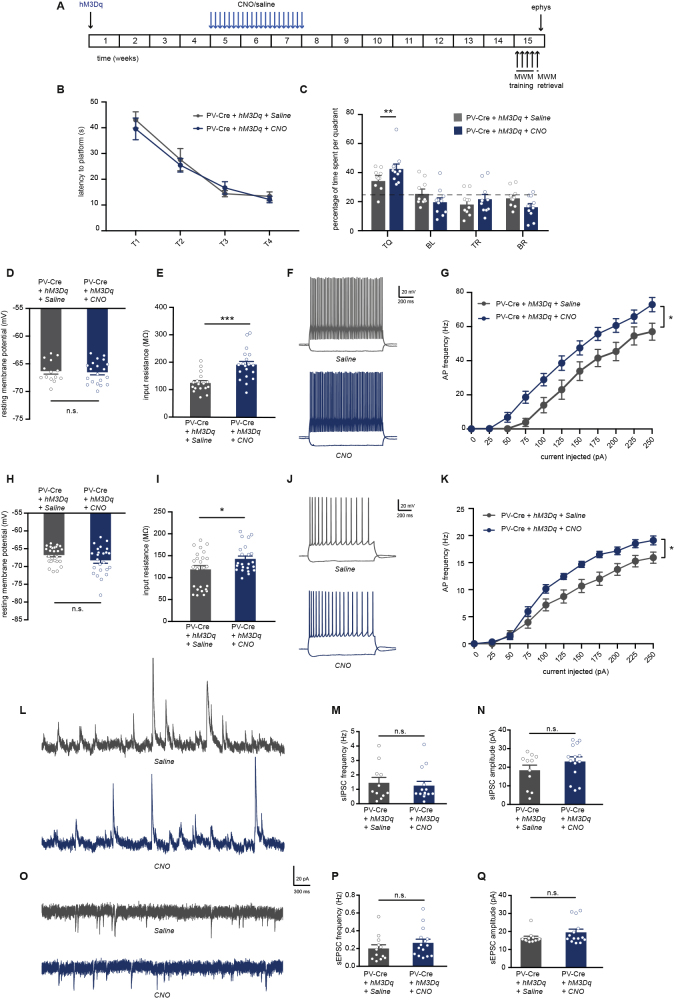
Figure 3.
Prolonged Chemogenetic Activation of Hippocampal PV Interneurons Induces a Hyperexcitable Hippocampal Network but Does Not Impair Spatial Memory on the Long Term
(A) PV-Cre mice were injected with hM3Dq virus at 8–10 weeks of age. After 4 weeks, CNO (1 mg/kg) or saline were i.p. injected daily for a period of 3 weeks. Behavioral testing and electrophysiological recordings were performed 8 weeks after discontinuation of CNO injections.
(B) Spatial learning was assessed measuring the latency to find the hidden platform on four consecutive training days (T1–4). PV-Cre mice that both expressed hM3Dq and had received CNO injections or saline injections showed significant learning during training (training two-way repeated measures ANOVA: n = 10 mice per group, F2,27 = 43.65, p < 0.001).
(C) During the one-minute probe trial, CNO-injected PV-Cre mice expressing hM3Dq spent significantly more time in the target quadrant (TQ) compared with PV-Cre mice receiving control saline injections (two-way ANOVA: n = 10 mice per group, F3,72 = 4.42, p = 0.006, post-hoc LSD test: ∗∗p = 0.009). Compared with chance level (dashed line), both saline-injected PV-Cre mice and CNO-injected PV-Cre mice spent significantly more time in the target quadrant (Student's t test: p < 0.01 for saline and p < 0.001 for CNO).
(D) PV interneuron resting membrane potential was not different between CNO-injected or saline-injected PV-Cre mice expressing hM3Dq (Student's t test: n = 14/20 cells from 4 mice per group, p = 0.776).
(E) PV interneuron input resistance was significantly increased in CNO-injected compared with saline-injected PV-Cre mice expressing hM3Dq (Student's t test: n = 14/20 cells from 4 mice per group, ∗∗∗p = 0.000).
(F) Voltage responses to 1 s hyperpolarizing or depolarizing current steps from a PV interneuron in saline-injected PV-Cre (gray) and CNO-injected PV-Cre (blue) mice.
(G) Average action potential (AP) frequency in response to 0–250 pA depolarizing current steps illustrating a significant increase in PV interneuron excitability in CNO-injected PV-Cre mice compared with saline-injected PV-Cre mice (group x current two-way repeated measures ANOVA: n = 14/20 cells from 4 mice per group, F1,42 = 4.32, ∗p = 0.044).
(H) Pyramidal neuron resting membrane potential was unaltered in CNO-injected PV-Cre mice compared with saline-injected PV-Cre controls (Student's t test: n = 25/24 cells from 5 mice per group, p = 0.123).
(I) Pyramidal neuron input resistance was significantly increased in CNO-injected compared with saline-injected PV-Cre mice expressing hM3Dq (Student's t test: n = 25/24 cells from 5 mice per group, ∗p = 0.031).
(J) Voltage responses to 1 s hyperpolarizing or depolarizing current steps from a pyramidal neuron in a saline-injected PV-Cre mouse (gray) or a CNO-injected PV-Cre mouse (blue).
(K) AP frequency in response to 0–250 pA depolarizing current steps illustrating a significant increase in pyramidal neuron excitability in CNO-injected PV-Cre mice compared with saline-injected PV-Cre controls (group x current two-way repeated measures ANOVA: n = 25/24 cells from 5 mice per group, F1,21 = 7.74, ∗p = 0.011).
(L) Example traces of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSC) recorded from hippocampal pyramidal neurons in saline-injected PV-Cre mouse (gray) or a CNO-injected PV-Cre mouse (blue).
(M and N) No significant alterations were observed in the frequency (M) or in the amplitude (N) of sIPSCs in CNO-injected PV-Cre mice compared with saline-injected PV-Cre controls (Mann-Whitney test: n = 11/14 cells from 4 mice per group, p = 0.727 and p = 0.267).
(O) Example traces of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSC) recorded from hippocampal pyramidal neurons in saline-injected PV-Cre mouse (gray) or a CNO-injected PV-Cre mouse (blue).
(P and Q) No significant alterations were observed in the frequency (P) or in the amplitude (Q) of sEPSCs in CNO-injected PV-Cre mice compared with saline-injected PV-Cre controls (Mann-Whitney test: n = 11/14 cells from 4 mice per group, p = 0.195 and p = 0.193). Values are mean ± SEM.