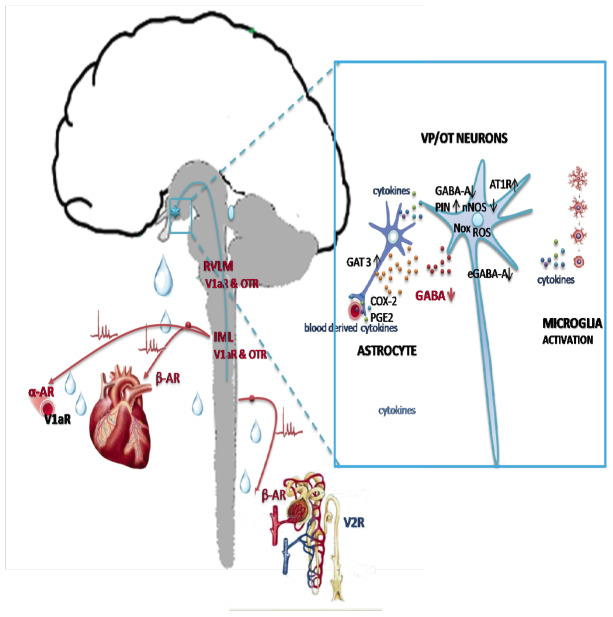
Fig. (4).
Hypothalamic targets in heart failure. Left: axonal projections of VP/OT neurons to neurohypophysis and rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) and intermediolateral column (IML) of the spinal cord involved in dual, peripheral and central control of the heart, vascular resistance and the kidneys. Right: molecules implicated in the dysregulation of VP and OT neurons. V1aR: vasopressin V1a receptor; OTR: oxytocin receptor; αAR: alpha adrenergic receptor; βAR: beta adrenergic receptor; AT1R: angiotensin II receptor type 1; GABA-gamma aminobutiryc acid; GABA-A: gamma aminobutiryc acid receptor type A at the synapse; eGABA-A: extra-synaptic GABA-A receptors; GAT 3: GABA transporter type 3; nNOS: neuronal NO synthase; PIN: protein inhibitor of nNOS; ROS: reactive oxygen species; Nox: NADPH oxidases; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; COX-2: cyclooxygenase type 2.