Fig. (2).
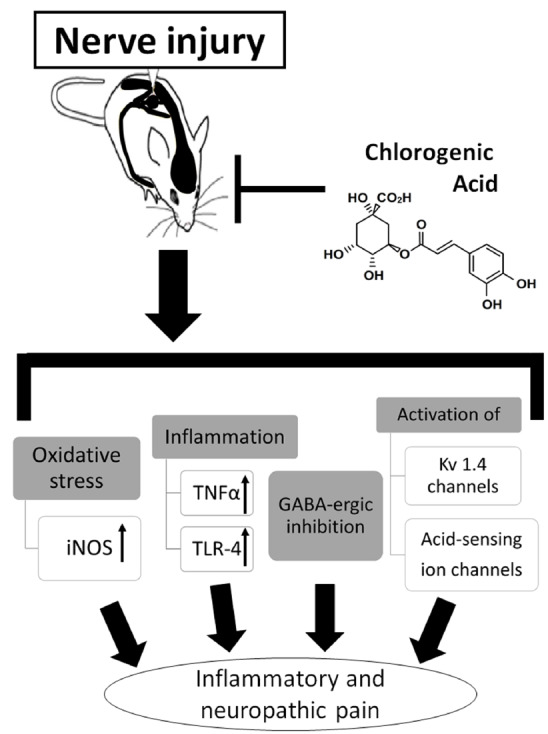
Possible mechanisms of chlorogenic acid in regulating inflammatory and neuropathic pain. CGA inhibits inflammatory and neuropathic pain; however, CGA does not alleviate acute pain. The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, and neurotrophic activities of CGA most likely underlie its antinociceptive effects. Furthermore, CGA-mediated antinociception does not affect motor performance, suggesting that CGA is not psychoactive.
