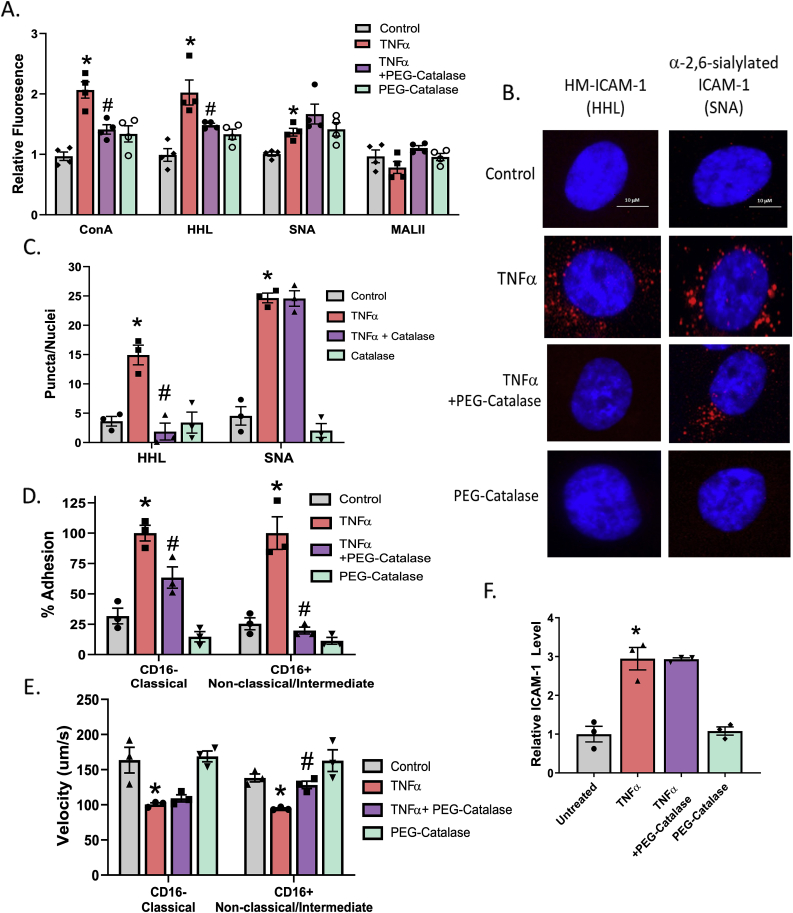
Fig. 4.
TNFα-induced HM-ICAM-1 formation and α-mannosidase activity inhibition can be reversed with PEG-Catalase. A. HUVECs treated with 100 units of PEG-catalase 30 min prior to TNFα treatment and lectin staining with ConA, HHL, SNA, and MAL-II was performed. * = p ≤ 0.05 compared to control; # = p ≤ 0.05 compared to TNFα by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 3 B. HUVECs were treated as described in A and subject to proximity-ligation assay (PLA) for HM- (HHL) and α-2,6,-sialylated (SNA) ICAM-1. Shown are representative images. Red puncta indicate positive staining for the ICAM-1 N-glycoform probed. C. Quantitation of red puncta from panel B. * = p < 0.05 compared to control; # = p ≤ 0.05 compared to TNFα by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 3. D. HUVECs were treated as described above and CD16− and CD16+ monocyte adhesion to the ECs was measured under flow. * = p < 0.05 compared to control; # = p ≤ 0.05 compared to TNFα by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 3. E. Monocyte rolling velocities calculated from (D). Data are mean ± SEM, n = 3. * = p < 0.05 compared to control; # = p ≤ 0.05 compared to TNFα by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. F. HUVECs were treated as described above and total surface ICAM-1 was measured via ELISA. * = p < 0.05 compared to control by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 3. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)