Fig. 1.
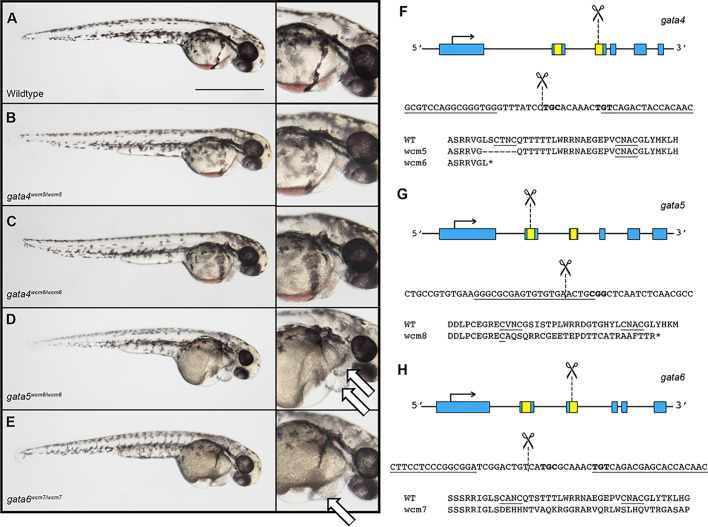
Mutation of gata4 is tolerated while mutations in gata5 or gata6 cause embryonic lethal cardiac defects. (A–E) Representative images of 2 dpf gata4, gata5, or gata6 homozygous mutants compared to wild type following TALEN (gata4 and gata6) or CRISPR (gata5) mediated deletion of the GATA zinc finger DNA-binding domain. (B,C) Gata4 homozygous mutants are phenotypically normal. (D,E) Gata5 and gata6 homozygous mutants develop severe pericardial edemas (indicated by white arrows in the far right panels) and fail to survive beyond 5–6 days. These phenotypes are 100% penetrant. Representative scale bar in A: 0.5 mm. (F–H) Schematic showing the structure, partial nucleotide sequence, and partial amino acid sequence for each of the gata4/5/6 mutant alleles. Zinc finger domains are shown in yellow and regions targeted for deletion are marked by dashed lines.