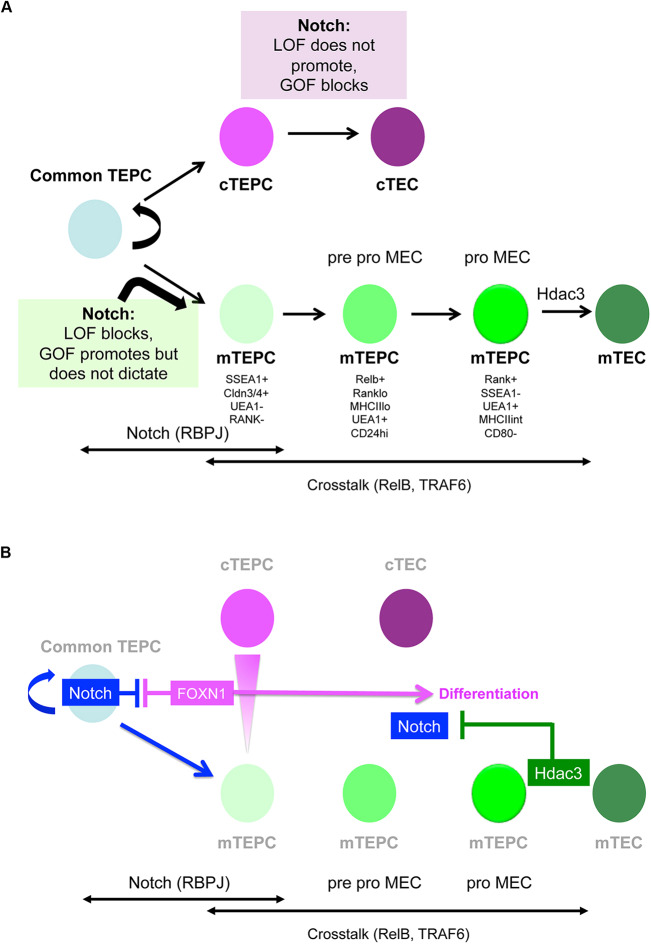
Fig. 7.
Model for Notch signaling regulation of early TEC development. Schematic diagrams presenting the model of early TEC development supported by the findings presented herein. (A) Notch signalling has an essential role in the differentiation of early fetal TECs: its loss of function results in mTEC hypoplasia, while its gain of function leads to TEPC maturation arrest. Notch activity precedes crosstalk-dependent further expansion and maturation of mTECs. (B) The Notch pathway in the context of a broader regulatory network. In early TEC differentiation, Notch influences and may be influenced by FOXN1, whereas it is suppressed by HDAC3 in postnatal mTECs.