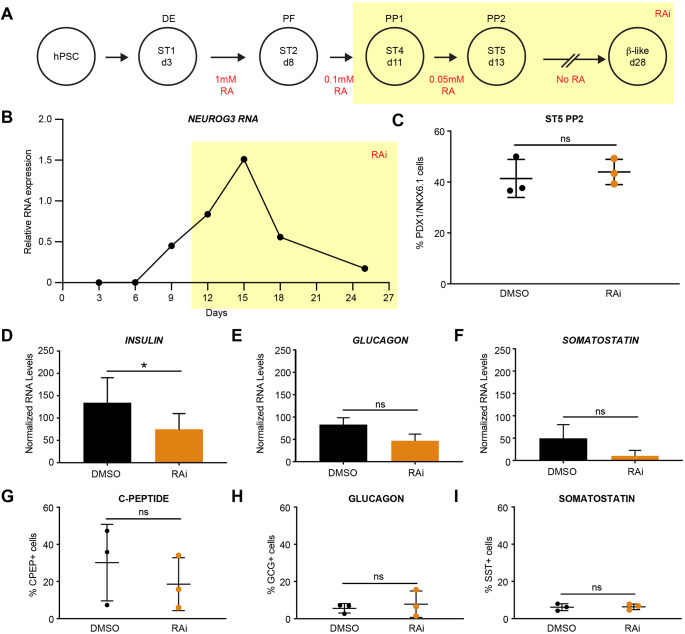
Fig. 3.
Human β cell differentiation requires RA signaling after posterior foregut formation. (A) Summary of human β cell differentiations with RA addition in red. Highlighted area (yellow) indicates when exogenous RA was removed from the media and RA inhibitor (RAi) was added. (B) RT-qPCR gene expression analysis of NEUROG3 expression, normalized to TBP. (C) Percentage of PDX1+/NKX6.1+ cells at stage 5 (ST5) of the differentiation with and without RAi treatment (n=3 per treatment, statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired parametric Student's t-test method; P>0.05 not significant). (D-F) RT-qPCR gene expression analysis of INS, GCG and SST expression at day 28, normalized to TBP for total RNA and CHGB for endocrine cells to control for differentiation efficiency (n=3 per treatment, statistical analysis was performed using a paired parametric Student's t-test method; *P<0.05 is significant). (G-I) Percentage of cells positive for C-peptide, glucagon and somatostatin by flow cytometric analysis (n=3 per treatment, statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired parametric Student's t-test method; P>0.05, not significant). All n values represent biological replicates. ns, not significant. Data are mean±s.d.