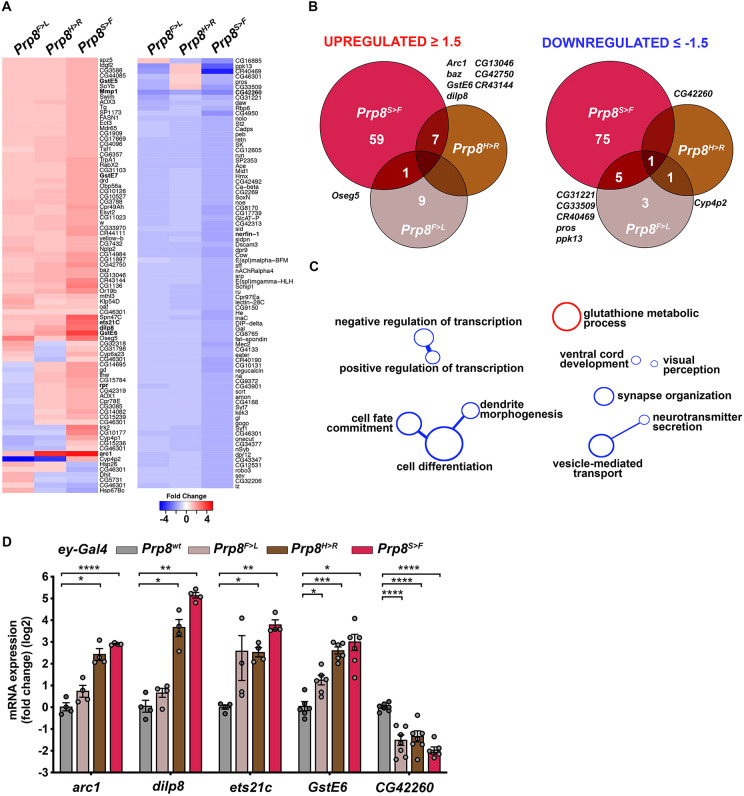
Fig. 6.
RP-Prp8 mutant variants induce stress and cytoprotective gene expression program. (A) The heatmap depicts genes significantly up- or downregulated following ey-specific overexpression of at least one of the RP-Prp8 mutant variants (|fold change|≥1.5, P<0.05) relative to those expressing Prp8wt. The expression changes of these transcripts in other experimental groups are also shown, but may not need to satisfy the criteria of P<0.05 significance. See Supplementary Dataset 1 for genes significantly changed. (B) Venn diagrams show overlap of genes significantly regulated (|fold change|≥1.5, P<0.05) in EADs expressing asymptomatic Prp8F>L or the two toxic RP-Prp8 variants, Prp8H>R or Prp8S>F. (C) Functional GO terms and clusters enriched among up- (red) and downregulated (blue) genes in ey>Prp8S>F-overexpressing EADs. (D) mRNA levels of stress-related and cytoprotective genes (arc1, dilp8, ets21c, GstE6) were significantly induced in response to ey-specific expression of Prp8H>R and Prp8S>F while CG42260 related to neuronal function was downregulated relative to ey>Prp8wt samples. RT-qPCR data are means±s.d., n≥4. Statistical significance was determine using unpaired t-tests with Welch's correction assuming unequal variance; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. The exact number and biological replicates per sample (n) and P-values are specified in Supplementary Dataset 2.