Fig. 5.
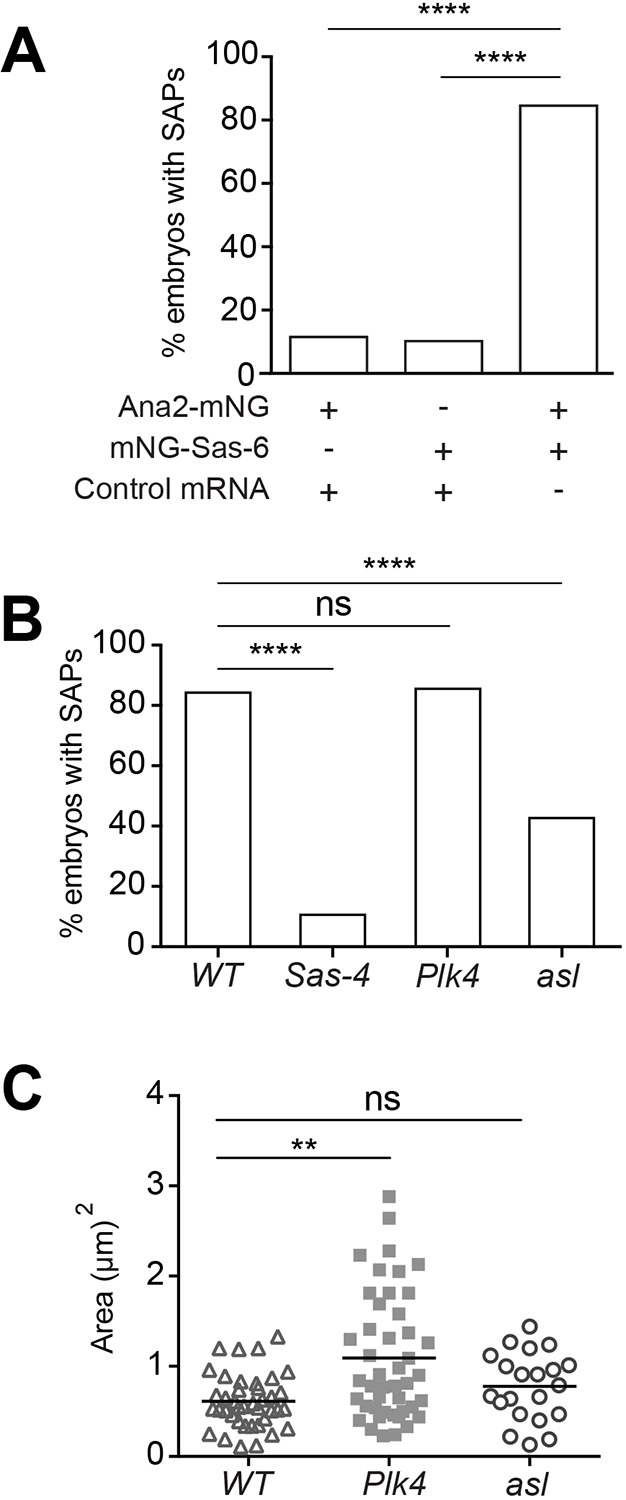
Efficient SAP assembly requires Sas-4 and Asl, but not Plk4. (A) Percentage of eggs that form SAPs upon the injection of mRNA encoding Ana2-mNeongreen, mNeongreen-Sas-6 or both (n=26, 39 and 52, respectively). Fisher's exact test was used to assess statistical significance. (B) Percentage of eggs laid by either WT, Sas4s2214, aslB46 or Plk4Δa mutant females that develop SAPs after co-injection of mRNA encoding Ana2-mNoengreen and Sas-6-mNeongreen (n=52, 55, 78 and 47, respectively). Fisher's exact test was used to assess statistical significance. (C) SAP size in eggs of the indicated genotype. Note that the SAPs are slightly larger in Plk4 mutant eggs, presumably indicating that Plk4 does influence some parameter(s) of SAP assembly, although it is unclear why the SAPs become slightly larger in the absence of Plk4. Each data point represents the average SAP size in an individual egg (N=1–366 SAPs per egg; n=21–45 eggs per genotype). The data was not normally distributed according to the D'Agostino and Pearson or Shapiro–Wilk normality test so a Kruskal–Wallis test was used to assess statistical significance. ns, not significant; **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
