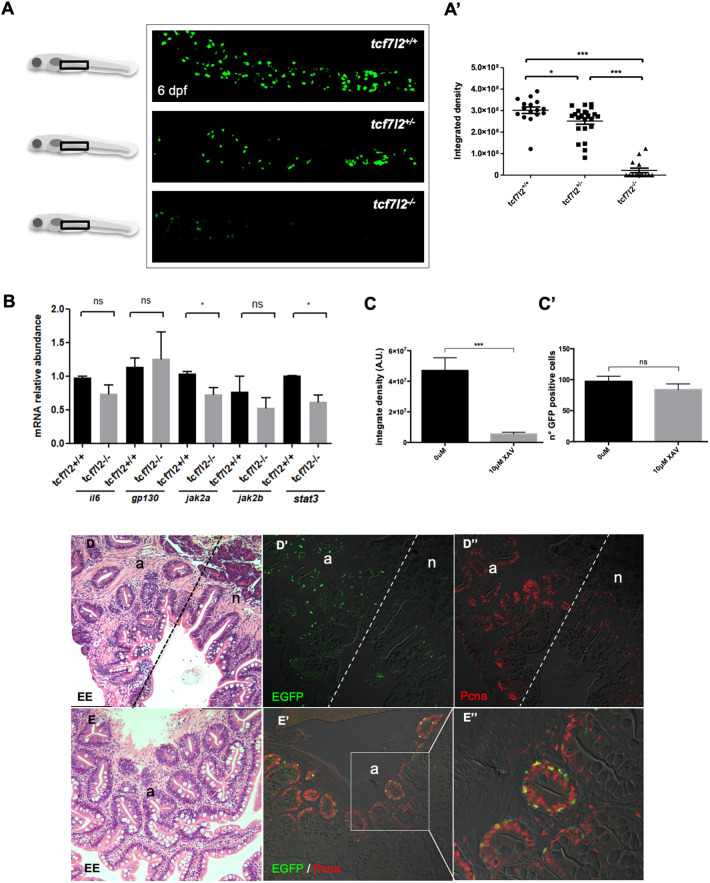
Fig. 7.
Tcf7l2 (Tcf4) is required for development of Stat3-responsive cells of zebrafish larvae intestine and the Stat3 pathway is activated ectopically in intestinal adenomas of apchu745 mutants. (A,A′) In vivo EGFP fluorescence in the intestine of 6 dpf Tg(7xStat3:EGFP)/tcf7l2hu892/hu892, Tg(7xStat3:EGFP)/tcf7l2+/hu892 and Tg(7xStat3:EGFP)/tcf7l2+/+ siblings (A) and measurement of integrated density (A′) (n=16). (B) qPCR analysis of il6, gp130, jak2a, jak2b and stat3 mRNA expression from tcf7l2+/+ and tcf7l2hu892/hu892 sibling larvae. (C,C′) Effect of XAV treatment on Tg(7xStat3:EGFP) embryos from 48 to 78 hpf: measurement of the integrated density of the fluorescence (C) and measurement of the number of GFP+ cells (C′). (D,E) Haematoxylin-eosin staining on paraffin embedded transversal section of zebrafish apchu745 intestine at 12 months post fertilization, displaying both normal tissue (n) and hyperplastic adenomas (a). (D′,D″) Staining of a sequential intestinal section of D using α-EGFP (green) (D′) and α-PCNA (red) (D″) Abs. (E′,E″) Double staining using α-EGFP Ab (green) and α-PCNA Ab (red) of a sequential intestinal section of E. All statistical analyses were performed by unpaired t-test. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001; ns, not significant. Error bars indicate s.e.m.