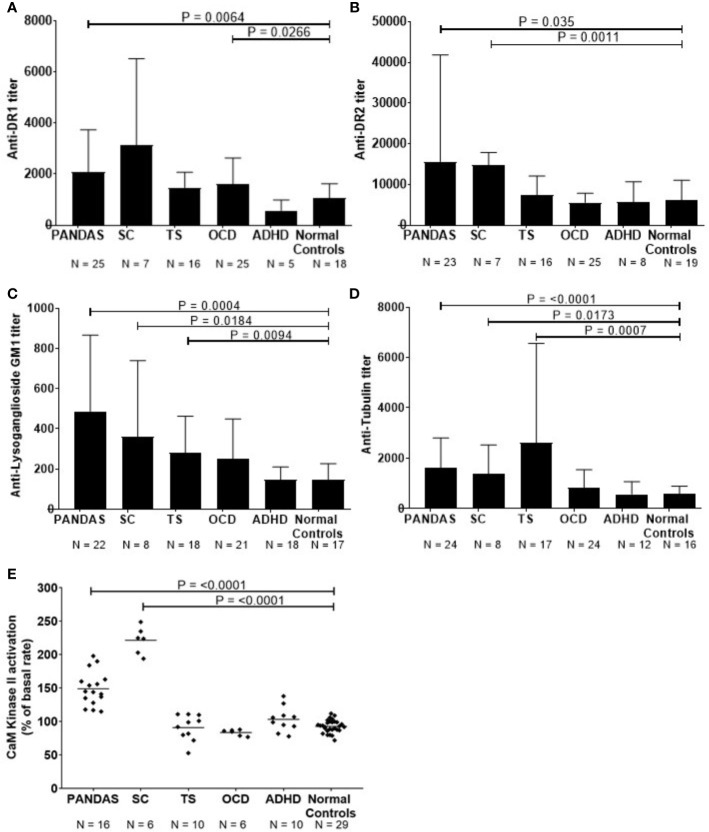
Figure 1.
Anti-neuronal autoantibody ELISA titers and CaMKII enzyme activation in childhood neuropsychiatric/movement disorders. (A). Anti-dopamine receptor D1 (D1R) IgG titers, (B). anti-dopamine receptor D2 (D2R) IgG titers, (C). anti-lysoganglioside GM1 IgG titers, (D). anti-tubulin IgG titers, and (E). %CaMKII enzyme activation in the human neuronal cell line SK-N-SH above basal level [Figure 1E adapted from (8) with permission from the Journal of Neuroimmunology, Elsevier]. Patients with specific neuropsychiatric/movement disorders include: pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with streptococcal infection (PANDAS, from first 50 cases at NIMH5), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Mann-Whitney non-parametric U test performed between each disease group and the normal controls group. An adjusted alpha level of 0.01 was used to account for multiple pair-wise comparisons made between case groups (five different groups) and the normal controls.