Figure 1.
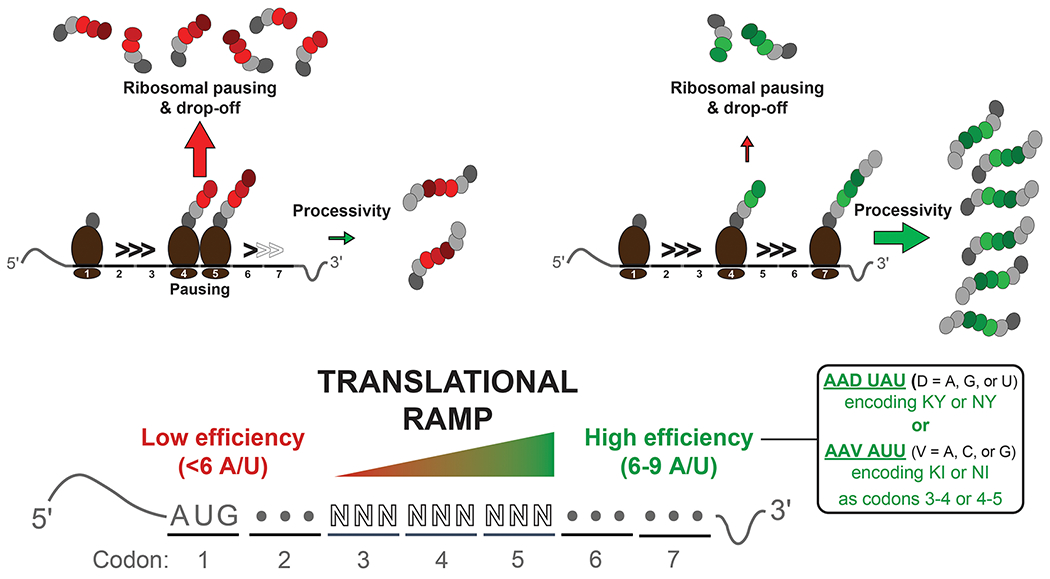
Codons 3–5 and their amino acids act as a translational ramp in a sequence-dependent manner. Low-efficiency sequences are associated with ribosomal pausing at codon 4 or 5 and termination of protein synthesis. In contrast, AU-rich sequences and the specified dipeptides (inset) favor high efficiency, leading to processive translation through codons 3–5 and an increased level of full-length polypeptide synthesis.
