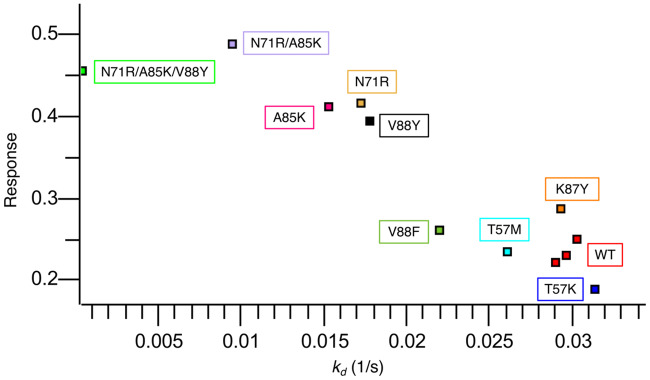
Fig 8. Single-concentration experimental screening of c-Raf-RBD variants binding to KRas using BLI.
c-Raf-RBD variants at 250 nM were allowed to associate with KRasGppNHp immobilized on a Ni-NTA OctetRed96 BLI tip for 180 s and then dissociation was measured and fitted for 120 s. All dissociation fits were performed in a local 1:1 model and showed strong agreement with the data, every fit having greater than a R2 of 0.99 and a χ2 lower than 0.01. The fitted dissociation rate constant (kd (1/s)) is plotted versus the response rate for each variant. Each point is labeled with its corresponding variant boxed in the corresponding color. A triplicate repeat was performed for the c-Raf-RBD wild-type (WT) variant (red). Variants fall into three groups: variants similar to WT (T57K in blue, T57M in cyan, WT in red, K87Y in orange, and V88F in forest green), variants better than WT (A85K in pink, N71R in sand, and V88Y in black), and variants with a response more than twice as large as WT (RK in purple and RKY in green). These results were used as a screen with the most promising variants being studied further by full titration BLI experiments (see Fig 10). The corresponding BLI response curves for this experiment are presented in S1 Figure.