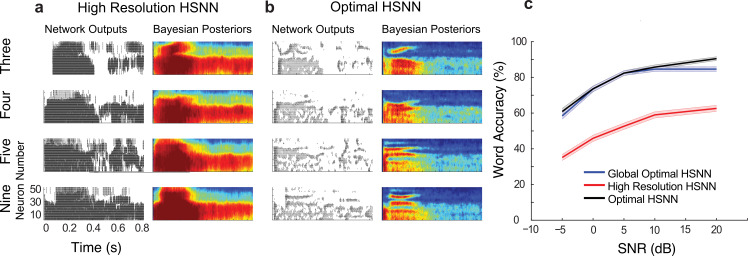
Fig 5. Optimal HSNN outperforms a high-resolution HSNN designed to preserve incoming acoustic information.
Sample network spike train outputs and Bayesian likelihood histograms for the words three, four, five, and nine are shown for the (a) high-resolution and (b) optimal HSNN at 5 dB SNR. The Bayesian likelihood histograms correspond to the average probability of firing at each time-frequency bin for each digit (averaged across all trials and talkers). The firing patterns and Bayesian likelihood of the high-resolution network are spatio-temporally blurred compared to the hierarchical network. (b) Details such as spectral resonances (e.g., formants) and temporal transitions resulting from voicing onset are accentuated in the hierarchical network output. (c) The optimal HSNN (maximize performance across all SNRs) outperforms the high-resolution network in the word recognition task at all SNRs tested (blue = optimal; red = high-resolution) with an average accuracy improvement of 25.7%. The optimal HSNN word recognition accuracy also closely matches the performance when the network is optimized and tested individually at each SNR (black, SNR optimal HSNN) indicative of a stable network representation.