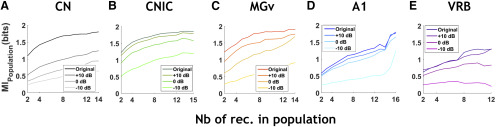
Figure 9.
Noise effects on the MIPopulation growth functions in each auditory structure. A–E, The curves display the noise effects on the MIPopulation growth functions for each structure and at each SNR (indicated by a gradient colors) in CN (A, in black), CNIC (B, in green), MGv (C, in orange), A1 (D, in blue), and VRB (E, in purple). In general, background noise largely altered the growth functions of the MIPopulation in each structure (but to a lesser extent in the CNIC). In the CN, noise induced a stronger reduction of the MIPopulation, which was clearly a function of SNR. In the CNIC, noise induced SNR-dependent reduction in the MIPopulation values, the reduction being modest at a +10 and 0 dB SNR but more important at a −10 dB SNR. In the MGv, noise progressively lowered the curves of the MIPopulation. In the cortex, the MIPopulation growth functions were not strongly impacted except at the −10 dB SNR.