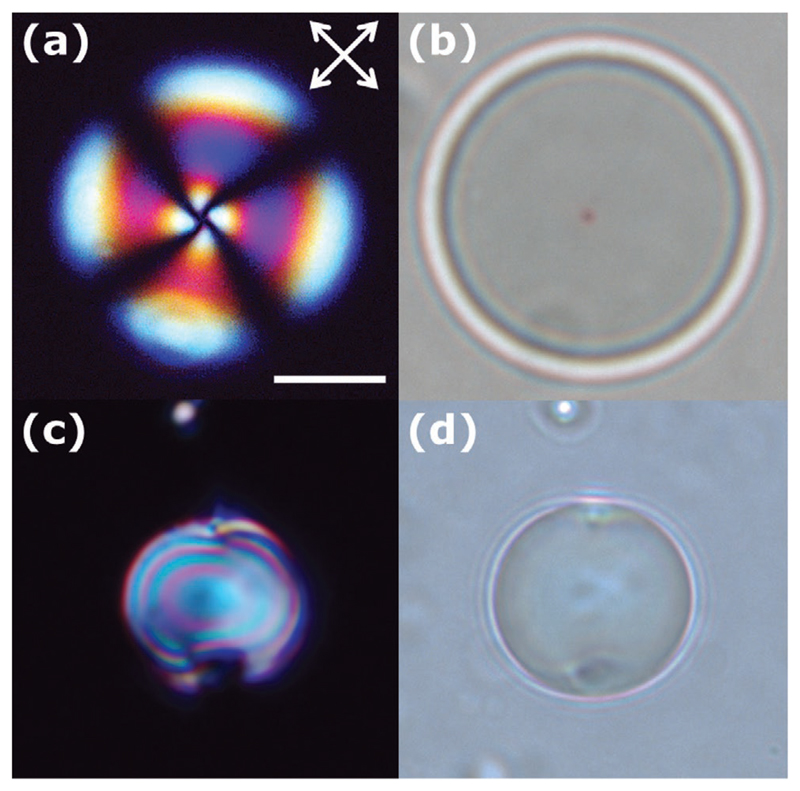
Figure 7.
a,b) Polarized light and bright-field microscopy images of nematic droplets with homeotropic anchoring. a) The extinction branches match the corresponding directions of the polarizers. b) Bright-field microscopy is used to visualize the core defect of the radial director profile named hedgehog and c,d) planar anchoring. c) The polarized light optical texture of the bipolar droplet depends on the position of the sample with respect to the crossed polarizers. d) Bright field microscopy enables the identification of the two surface defects, named boojums. The scale bar corresponds to 10 μm.