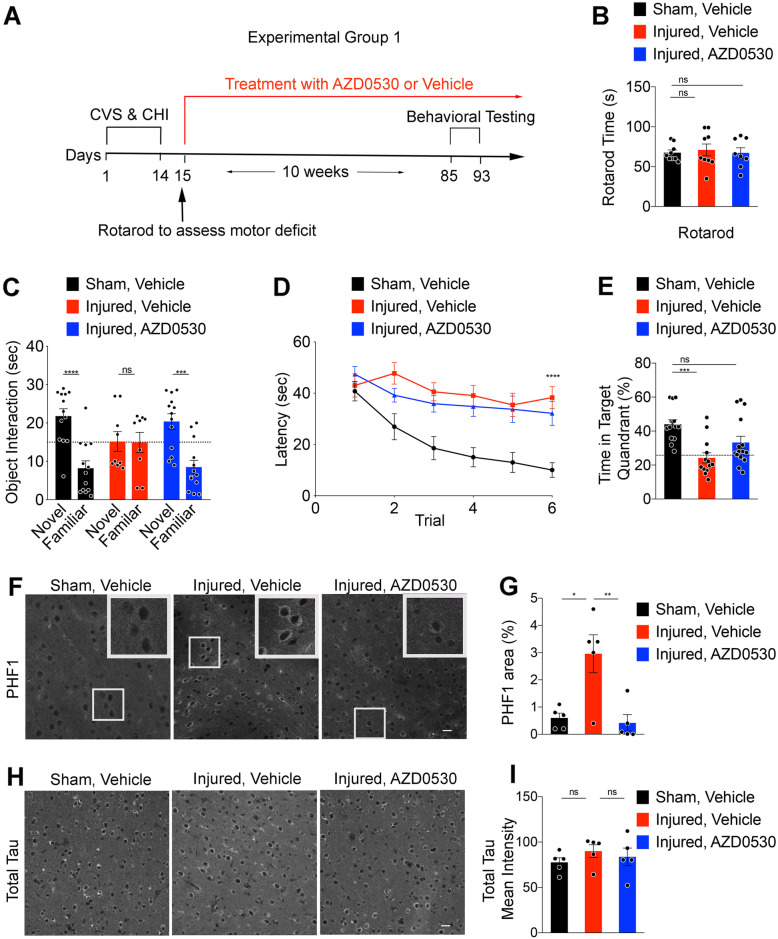
Fig. 5.
Fyn Inhibition Rescues Memory Deficits and Prevents Phospho-Tau Accumulation after Repeated Mild Head Injury Combined with Chronic Stress. (a) Timeline for mice undergoing 14 days of chronic variable stress (CVS) and closed head injury (CHI) or Sham CVS & CHI paradigm. On Day 15, Rotarod testing was done to assess motor impairment in a subset of mice. The mice were treated with either AZD0530 (5 mg/kg/d) or Vehicle treatment for 10 weeks starting 24 h after the final day of injury. This was followed by one week of behavioral testing at 7 months of age, including novel object recognition test and Morris water maze prior to perfusion and immunohistochemistry. (b) Rotarod prior to the treatment using the WT Sham and Injured groups at 4.5 months of age. One-way ANOVA, p > 0.05. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 8–9 /group, each dot is one mouse. (c) Novel object recognition test of 7-month-old WT mice from Sham Vehicle-treated (SV), Injured Vehicle-treated (IV), and Injured AZD0530-treated (IA) groups. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 9–13/group, each dot represents one mouse. Two-way ANOVA, p = 0.007 for interaction of group with object; Sidak’s multiple comparison test: Novel vs Familiar for Sham Vehicle (SV), ****p < 0.0001; Injured Vehicle (IV), p = 0.99; Injured AZD (IA), ***p = 0.0002. (d) Latency to reach a hidden platform in Morris water maze across 6 blocks of 4 swims of 7-month-old WT mice from SV, IV, and IA groups. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 14–17 /group. Repeated measures one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: SV vs IV, ****p < 0.0001; IV vs IA, p = 0.98; SV vs IA, ****p < 0.0001. (e) Morris water maze probe trial showing time in the Target quadrant of 7-month-old WT mice from SV, IV, and IA groups. Dashed line indicates random chance performance of 25% in the target quadrant. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 13–15 /group, each dot is one mouse. Two-tailed Wilcoxon signed rank test for non-Gaussian distribution versus random chance: SV, ***p = 0.0001; IV, p = 0.47; IA, *p = 0.046. One way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: SV vs IV, p = 0.0003; IV vs IA, p = 0.12; SV vs IA, p = 0.05. (f) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining for PHF1 of coronal cerebral cortex sections within 0.5–1 mm medial to the site of injury in 7.5-month-old WT mice from SV, IV, and IA groups. Boxed area is shown at higher magnification inset. Scale bar, 20 μm. (g) Quantification of PHF1-positive area within 0.5–1 mm medial to the site of injury in 7.5-month-old WT mice from SV, IV, and IA groups. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 5 /group, each dot is one mouse. One way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: SV vs IV, *p = 0.0077; IV vs IA, **p = 0.0046. (h) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining for total Tau in the cortical sections at the same region as F in 7.5-month-old WT mice from SV, IV, and IA groups. Scale bar, 20 μm. (i) Quantification of total Tau mean intensity at the same region as F in 7.5-month-old WT mice from SV, IV, and IA groups. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 5 /group, each dot is one mouse. One way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test