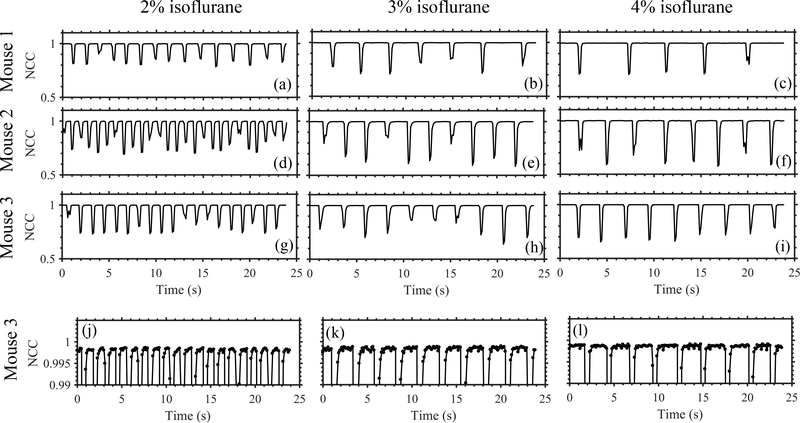
Fig. 3:
Respiration rate analysis on three mice at different anesthetic levels using B-mode cross-correlation. Motion due to inhalation and exhalation appeared as reductions in temporal NCC profiles. Increasing the anesthetic level decreased the respiration rate and increased the duration of quiet zones in respiration cycles. Plots (g)-(i) are reproduced in (j)-(l), respectively, with a smaller y-axis range to visualize the variation in NCC within the quiet zones.