Figure 1.
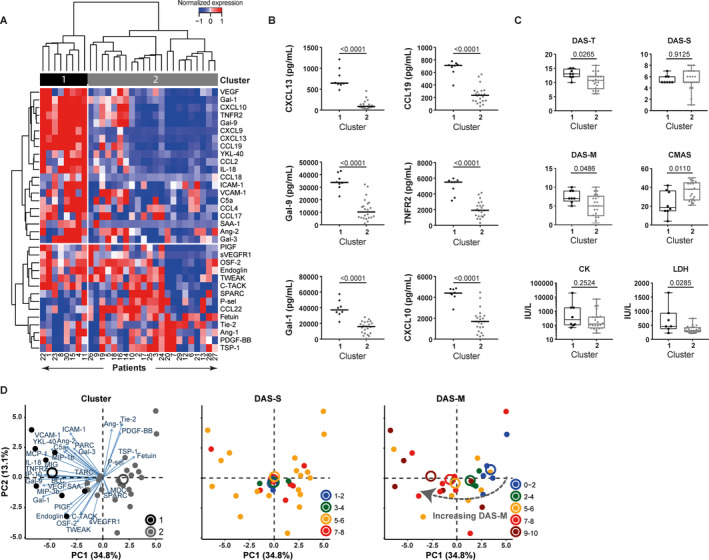
Association of heterogeneous biomarker profiles with differences in clinical disease activity in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis (DM). A panel of biomarkers for endothelial dysfunction and inflammation was measured by multiplex assay in the serum of 30 treatment‐naive juvenile DM patients (discovery cohort). A, Unsupervised hierarchical clustering (by Euclidian distance and Ward's method) of 30 patients in the discovery cohort based on serum levels of 34 biomarkers (mean‐centered and scaled values) yielded 2 distinct patient clusters (clusters 1 and 2). Values at the bottom represent unique patient identifiers (not ranked). B, Serum levels of the 6 markers most significantly different between cluster 1 (n = 8) and cluster 2 (n = 22) were compared by Mann‐Whitney U test, with correction for multiple comparisons based on the false discovery rate. Symbols represent individual patients; horizontal lines show the median. C, Clinical scores for global Disease Activity Score (DAS‐T), skin Disease Activity Score (DAS‐S), muscle Disease Activity Score (DAS‐M), Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale (CMAS) score, and muscle enzyme levels (creatine kinase [CK] and lactate dehydrogenase [LDH]) were compared between the 2 clusters. P values were determined by Mann‐Whitney U test. Results are shown as box plots, where the boxes represent the 25th to 75th percentiles, the lines within the boxes represent the median, and the lines outside the boxes represent the 10th and 90th percentiles. D, Principal components (PC1 and PC2) analysis based on the 34 mean‐centered markers shows patients stratified by cluster, DAS‐S scores, and DAS‐M scores. Circles with different colors represent clusters 1 and 2 or ranges of DAS‐S and DAS‐M scores. Closed circles represent individual patients, while open circles represent cluster centers. VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; Gal‐1 = galectin‐1; TNFRII = tumor necrosis factor receptor type II; YKL‐40 = chitinase‐3–like protein 1; IL‐18 = interleukin‐18; ICAM‐1 = intercellular adhesion molecule 1; VCAM‐1 = vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; SAA1 = serum amyloid A 1; Ang‐2 = angiopoietin‐2; PIGF = placental growth factor; sVEGFR1 = soluble VEGF receptor 1; OSF‐2 = periostin; TWEAK = TNF‐related weak inducer of apoptosis; C‐TACK = cutaneous T cell–attracting chemokine; SPARC = secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; P‐sel = P‐selectin; Tie‐2 = angiopoeitin‐1 receptor; PDGF‐BB = platelet‐derived growth factor BB; TSP‐1 = thrombospondin‐1.
