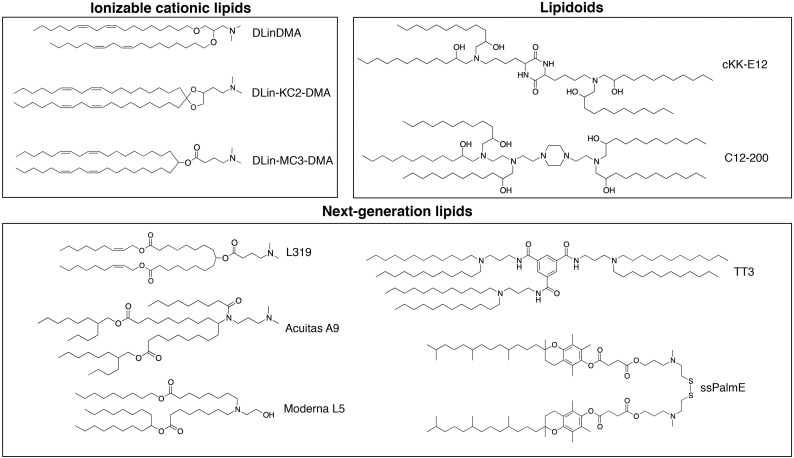
Fig. 3.
Ionizable cationic lipids or lipid-like materials (lipidoids) enabling gene therapy in the liver. Various lipid-like materials have been developed for nucleic acid delivery. The headgroups contain tertiary amines which become protonated under acidic pH and have typically no charge at neutral pH. The lipid tails contribute to making the molecule sufficiently hydrophobic to promote incorporation into LNPs while endowing either stabilizing or destabilizing properties. The above lipids are classified into three broad categories: (i) ionizable cationic lipids such as DLinDMA [133], DLin-KC2-DMA [30], and DLin-MC3-DMA [31]; (ii) lipidoids like cKK-E12 [134] and C12-200 [29]; and (iii) next- generation lipids including the biodegradable molecules L319 [130], TT3 [135], and ssPalmE [136] as well as lipids from proprietary libraries belonging to Acuitas (A9) [137] and Moderna (L5) [138].